Valve may be preparing to merge the Chinese and global versions of Steam. If this happens, many developers will no longer be able to sell games in China without the approval of the local government (now only dozens of foreign titles are licensed per year).Prerequisites for the merger and possible consequences

Pavel Djundik, the creator of SteamDB, discovered a new interface for developers in the Steam code.
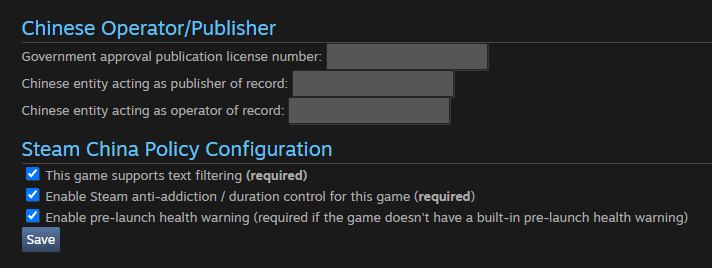
It is a form that must be filled out for the release of the game in the Chinese version of the store.
Developers must specify the license number obtained and the local publisher. To sell projects on Steam China, you must also enable the text filtering function and limit the amount of playing time.
The new interface that Jundik discoveredFormer game designer and gaming expert Simon Carless believes that this may indicate a potential merger of the two versions of the store.
This is hinted at by the beta testing of chat filtering, which Valve launched in August and which, according to Carless, is partly necessary for the games to enter the Chinese market.
In the absence of official confirmation from Steam, it is impossible to say for sure about the merger. However, in the case of a complete merger of stores, most developers will face a difficult choice: go through the grueling process of obtaining a license or completely abandon the Chinese market.
How does Steam China work now?Valve launched the Chinese version of its store together with the publisher Perfect World in 2019.
Steam China exists separately from the international version and includes only games licensed by the local government.
At the same time, now Chinese residents can still use global Steam, and developers often prefer not to get involved with obtaining the necessary licenses — primarily due to bureaucratic difficulties and additional financial costs.
The process of obtaining a license and the main difficultiesThe license costs $5,000, and the issuance is handled by the National Press and Publications Administration (NPPA).
As Adria Carrasco, founder of Another Indie, notes, approval has to wait 9-14 months, receiving numerous refusals and dealing with censorship.
Such conditions make it almost impossible to obtain a license for indie developers. However, even among large companies, the approval rate remains low.
According to Daniel Ahmad, senior analyst at Nikko Partners, 1,385 local games received licenses in 2019, and another 1,350 will be approved by the end of this year. At the same time, we are talking about titles on all platforms, including mobile.
Things are even worse with foreign projects. Last year, the NPPA approved only 185 games, including 32 PC projects. Ahmad notes that this year the total number of approved games from foreign studios will not reach 100.
Considering that now NPPA is busy checking iOS games (42 thousand projects were removed from the Chinese App Store in the summer), most titles on Steam risk not waiting in line and being left without a license.
Share and significance of Chinese revenueCarless analyzed the data of games on Steam that he has access to.
In the presence of localization, the share of Chinese revenue usually fluctuates around 10-22% and averages about 16%. At the same time, local users generate only 1-2% of sales for projects with a large amount of text and without translation into Chinese.
It is important to keep in mind that there are regional prices in China, and games on Steam China are on average 60% cheaper than in the USA. Carless also notes that Chinese users are twice as likely to make refunds.
Thus, the loss of the Chinese audience may not be as catastrophic as it seems at first glance. As an example, Carless cites the game Meteorfall: Krumit’s Tale, 27% of sales of which are in China. However, in reality, this is “only” 16-18% of total revenue.
Also on the topic:
- China intends to support games that reflect local culture and valuesSteam algorithm: what factors directly affect its operation and game sales
- Chinese developers announced a boycott of Huawei and Xiaomi stores due to high commission
- Is there any news?
Share it with us, write to press@app2top.ru