Semenov&Pevzner Law Firm has prepared a global report on legal conflicts in the gaming industry over the past six months.
The review was prepared by Alyona Kuzmina, Senior Associate at Semenov&Pevzner, and Vadim Kocheshev, Associate Associate at Semenov&Pevzner.
Alyona Kuzmina and Vadim Kocheshev
The work is divided into five parts:
- copyright;
- means of individualization;
- patent rights;
- cheats;
- other cases.
The previous review (July — December 2022) can be found here.
Copyright
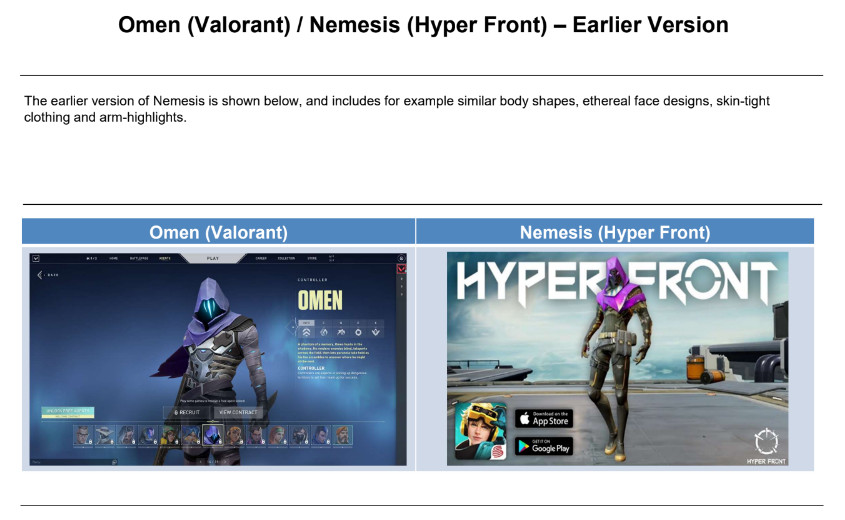
1. Riot Games has filed several lawsuits against NetEase due to violation of rights to Valorant
According to Polygon, Riot Games has filed lawsuits against the Chinese publisher NetEase, claiming that the Hyper Front mobile shooter infringes the copyright of its game Valorant.
Riot Games has filed lawsuits in the UK, Germany, Brazil and Singapore. In the claims, the applicant notes the similarity of characters, cards, weapons, spells, skins for weapons and weapon statistics.
After receiving the claim, NetEase changed the appearance of some Hyper Front characters:
All the lawsuits are the same in context, but they take into account the peculiarities of the copyright norms of each country. The lawsuit filed in an English court notes that Hyper Front “copies the most essential parts of the Valorant game.”
Both Hyper Front and Valorant are shooters in which teams of five players fight each other. Valorant was published in 2020 on PC, in 2021 its audience was estimated at 14 million players per month. Hyper Front was released in 2022 on Android and iOS. There are no official statistics on the average number of Hyper Front players, but according to Google Play, the game has more than a million downloads and more than 48,000 ratings.
The interesting question remains whether the national courts of Great Britain, Germany, Brazil and Singapore will accept the claims of Riot Games for consideration. Previously, the company has already had several unsuccessful attempts to sue another Chinese developer (Moonton) for copyright infringement in US courts. Then the California court refused to consider the application due to improper jurisdiction and indicated that the case should be transferred to China.
2. Nintendo won a copyright infringement lawsuit against the Dstorage website
The Paris court sided with Nintendo in a dispute with the operator of the file-sharing site Dstorage. The court found Dstorage responsible for not removing or blocking access to pirated copies of Nintendo games. Copies were distributed through a file hosting site 1fichier.com .
The court ordered Dstorage to pay compensation to Nintendo in the amount of €424,750, as well as €25,000 in court costs.
“Nintendo is pleased with the decision of the Paris Court of Appeal, as it once again makes it clear that file sharing services such as Dstorage (1fichier) are liable to French law for refusing to remove or block access to illegal copies of video games, despite the claim, and must remove or block such content, and may also be required to pay compensation to copyright holders whose exclusive rights have been violated,” Nintendo commented on the court decision.
The Korean company Nexon sued the Ironmace studio, which developed the PvPvE action game Dark and Darker. She accused the developers of disclosing trade secrets and stealing the code and assets of the P3 game.
In its lawsuit, Nexon pointed out that Ironmace executives Terence Seungha Park and Choi Joo-hyun used to work at Nexon and were engaged in a game called P3, which is substantially similar to Dark and Darker. According to the company, its former employees illegally gained access to the P3 source code, as well as audio-visual and other materials developed by Nexon at great expense of time and money. Nexon noted that it took Ironmace only nine months to release a demo of Dark and Darker. The studio managed to do this thanks to the stolen materials from P3.
In the lawsuit, Nexon also pointed out the similarities of some characters from P3 and Dark and Darker:
Example from the lawsuit
Nexon demanded damages and the return of all materials related to the P3 project.
Although both companies are registered in South Korea, the lawsuit was filed in a Washington court. The reason is that the testing of the game Dark and Darker was carried out on the Steam platform (owned by Valve with an office in Bellevue, Washington), and the marketing activities for the game were partially aimed at American users.
Ironmace planned to release the full version of Dark and Darker by the end of 2023. However, the game was removed from Steam after receiving Nexon’s notification. In February of this year, Ironmace publicly stated that it did not use other people’s IP assets in the development of its game, and their source code was written from scratch.
At the moment, the case is being considered in court.
4. NetEase won the court against the Alibaba Group division in the Invincible plagiarism case
A Chinese court has found that the Three Kingdoms Tactics mobile game from Ejoy, a division of Alibaba Group, infringed the copyright of the Shuai Tu Zhi Bin strategy (known outside China as Invincible). He awarded NetEase compensation in the amount of $7.2 million.
According to the court decision, Ejoy is obliged to remove 79 elements copied from Shuai Tu Zhi Bin from Three Kingdoms Tactics. At the same time, the court refused to completely restrict access to Three Kingdoms Tactics.
Representatives of Ejoy said they would challenge the court’s decision in Guangzhou. If the defendant loses in the appeal, the amount of compensation awarded will be the largest awarded in Chinese courts in relation to video games.
Three Kingdom Tactics is Alibaba’s most profitable game. According to App Magic, it has earned more than $1.97 billion from in-game purchases since launching in 2019.
Means of individualization
1. Companies producing chairs for professional gamers are suing for trademarks in the USA
The plaintiff, GT Racing, registered the trademark with the US Patent Office (USPTO). The defendant, GT Omega, filed an application to challenge the trademark registration with the US Patent Litigation Chamber (Trademark Trial and Appeal Board), due to the confusingly similar GT Racing trademark with the GT Omega trademark and the risk of misleading consumers. The U.S. Patent Litigation Chamber canceled the registration of GT Racing due to the earlier priority date of GT Omega. The Court also recognized the similarity of trademarks to the extent of confusion, since they were registered in relation to similar goods.
GT Racing disagreed with the chamber’s decision and filed a lawsuit in the federal court of Virginia, presenting evidence of the distinctive ability of its designation.
In the process, the parties concluded a settlement agreement on the coexistence of trademarks, according to which each party was granted the right to use its trademark, but with some restrictions on use in social networks in order to avoid misleading.
A few months later, GT Omega filed a new lawsuit in court due to the fact that GT Racing does not comply with the terms of the settlement agreement regarding the promotion of the GT Racing brand in social networks. The court agreed with GT Omega’s arguments and collected legal costs from GT Racing in favor of the applicant.
GT Racing has filed an appeal against the latest court decision.
Patent rights
1. Konami is suing Cygames for patent infringement in the game Uma Musume Pretty Derby
In March 2023, the Japanese publisher Konami filed a lawsuit in the Tokyo District Court against the mobile developer Cygames in connection with patent infringement in the popular simulation game Uma Musume Pretty Derby. The publicly available material does not specify which patent the controversial game violates.
According to a document published by the parent company Cygames, Konami demands compensation in the amount of $ 30 million and a ban on the development, use and promotion of the game.
Cygames has released an official statement in which it said that it had been negotiating with Konami about the exclusive rights to the patent. The negotiations, however, did not lead to a positive result. Cygames also declared the purity of its rights to the game Uma Musume Pretty Derby, as well as that the game will not be removed from the stores for the duration of the proceedings.
Cygames was founded in 2011 by CyberAgent. She has developed mobile games such as Shadowverse and Princess Connect! Re:Dive.
Cheats
1. Bungie won the court against AimJunkies
Back in 2021, Bungie (the developer of Destiny 2) filed a lawsuit against AimJunkies, the creator of cheats for games. It follows from the lawsuit that AimJunkies violated the plaintiff’s copyright by using the original game code to create cheats. In the last review, we talked in more detail about the plot of this case.
Despite the fact that Bungie was on the verge of losing, in February 2023, the court case ended in its favor. The court ruled that AimJunkies violated the DMCA and used third-party software to circumvent the protection of developers, and found AimJunkies guilty of illegally selling cheat codes.
The owners of the AimJunkies website are obliged to pay damages in the amount of $3.6 million and $700 thousand in court costs.
2. Activision won a dispute against the developer of cheats EngineOwning
In the last review, we wrote that Activision filed a lawsuit against EngineOwning, a seller of cheats for online shooters, in the U.S. District Court of the Central District of California on January 4, 2022. The company stated that the sale of cheats not only brought it material losses, but also caused reputational losses.
The lawsuit states that EngineOwning uses the popularity of the shooter for personal gain and profit by implementing cheats, hacks and other malicious software, which, in turn, negatively affects the gaming experience of Call of Duty users.
Earlier, Activision released a special anti-cheating supplement RICOCHET, with which over 500 thousand accounts of cheaters in Call of Duty were blocked. However, EngineOwning found a way to bypass anti-cheating software and started selling cheats for Call of Duty.
In the claim documents, requirements are also imposed on those who implement cheats, in particular to users of Bonsai, Homie, NOL3X. In addition, Activision has filed claims against a number of fictitious companies and individuals associated with EngineOwning and its business selling cheats in various jurisdictions.
In January 2023, the court awarded Activision $3 million to be recovered from the owners of EngineOwning. The court’s decision states that “the creators of cheats undertake to stop developing software that promotes circumvention, manipulation or obtaining other unreasonable advantages over other players.” The decision concerns not only the Call of Duty title, but also other Activision games, for example, Overwatch 2.
Other cases
The US Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has found Epic Games guilty of violating the US law on personal data of children under 13 (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act, COPPA). She issued an order to the Fortnite developer to pay $245 million to users to settle charges of using so—called “dark patterns” – gaming techniques to persuade underage players to make unwanted purchases or other unauthorized expenses.
In a notice sent in December 2022, the FTC alleged that Epic Games used various tricks in Fortnite in order to force consumers of all ages to make unintentional in-game purchases. Fortnite’s control buttons were contradictory and inconsistent and could mislead underage users, which often led to unwanted write-offs when just one button was pressed. The company also made it easier for children to make purchases in the Fortnite game without requiring parental consent. According to the FTC, Epic Games also blocked user accounts challenging unauthorized spending through personal banking systems.
In accordance with the FTC’s order, Epic Games is also required to pay $ 345 million, which will be used to refund funds to users. Epic Games will not be able to charge users using “dark patterns” or otherwise charge them without obtaining their express consent. In addition, the FTC order prohibits Epic Games from blocking users’ access to their accounts when challenging unauthorized expenses.
Recall that COPPA is a law on the protection of personal data of children under 13 years of age. It obliges online services to request the consent of parents or legal representatives of the child when collecting and processing personal data of such users. Mobile games, video games, social networks, forums and other online services are subject to the law, even if their developers are not residents of the United States. The fact that the service is available in the USA is enough.
In February of this year, a 204-page art book was leaked, which was supposed to be released with a special version of the game Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom. Copies quickly spread to Discord.
Nintendo’s lawyers investigated the leak, which led to one server belonging to Discord. In February, Nintendo asked Discord to remove the artwork.
In April 2023, Nintendo filed an application for a court order in a California court demanding that Discord disclose the data, names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses of a user under the nickname Julien#2743, who originally posted illegal content.
This isn’t the first time Nintendo has tried to identify a user who infringes on the company’s copyrights. In 2019, after the leak of guides on the passage of Pokemon Sword and Shield, which were posted on Reddit, Discord and 4chan, Nintendo also conducted a special investigation. The found users were obliged to pay Nintendo $ 150 thousand.
3. The British antimonopoly authority opposed the deal between Microsoft and Activision Blizzard, the European Commission approved the deal
In April, the British antitrust regulator published a report in which it concluded that the deal between Microsoft and Activision Blizzard would harm the cloud gaming market, innovation and choice opportunities for players. Earlier, the US antimonopoly authority also opposed the deal, which in December filed a lawsuit to block the deal.
In May, the European Commission made the opposite decision. She approved the largest deal in the gaming industry, considering that it would not affect competition, since Microsoft would allow other game publishers to have access to Activision Blizzard products for 10 years. The head of the European Commission, Margrethe Vestager, pointed out that the deal will allow the cloud gaming market to grow, which now accounts for only 1-3% of the entire gaming market.
Recall that Sony actively opposes this deal. She fears that giving Microsoft control over Activision Blizzard games will have serious negative consequences for gamers and the future of the gaming industry. According to Sony, Microsoft may stop releasing new Activision Blizzard games on competing platforms, including PlayStation consoles. All this will cause significant damage to Sony.
4. The Quebec Supreme Court has accepted a class action lawsuit against Epic Games
Epic Games has filed a class action lawsuit over Fortnite. The lawsuit specifies several groups of persons who filed a class action: those who experience addiction, manifested in a negative impact on their personal, family, social, educational and professional spheres of life, and minors who made purchases of in-game items using the virtual currency V-Bucks in Fortnite.
This case may be the first for Quebec, in which the court will consider the legality of the purchase of virtual items by minors without parental consent.
There are not so many court disputes about the recognition of a video game as addictive at the moment. As an example, we can cite the case of Craig Smallwood against NCSOFT, the developer of Lineage II. As a result of the case, the court sided with Smallwood and ordered the Korean company to reimburse the legal costs of treatment.
In our opinion, the decision in this case can create a precedent and set a global trend for changing the mechanics of video games in order to reduce the “dependence” of gamers.
The possibility of addiction to video games has been a topic of discussion lately. It is worth noting that after the World Health Organization recognized “gaming disorder” as a disease, the governments of many countries began to take measures regarding the access of minors to games. So, in August 2022, the Takamatsu District Court in western Japan confirmed the constitutionality of a local decree that established restrictions on video games to combat gaming addiction. In 2021, the Chinese authorities also limited the time that children and teenagers can spend on online games: gaming platforms can provide services to minors only from 8 to 9 pm on Fridays, weekends and official holidays.
5. A Canadian judge stated that loot boxes cannot be knowingly illegal
Plaintiff Mark Sutherland accused Electronic Arts (EA) of unfair and deceptive actions contrary to the British Columbia Consumer Protection Act. Sutherland filed a lawsuit on behalf of all residents of British Columbia who have paid for loot boxes in more than 70 Electronic Arts games since 2008.
In the lawsuit, Sutherland claims that EA, by selling loot boxes, “conducts illegal gambling-related activities, which is a violation of section 7 of the Criminal Code.”
The judge concluded that Sutherland’s claim should be accepted for consideration. But he rejected the accusation that loot boxes in EA games are an element of gambling. According to the court, Sutherland’s arguments about gambling do not correspond to reality, since loot boxes are sold only for in-game currency and they cannot be officially exchanged for real money.
Note that the issue of attributing loot boxes to gambling is solved differently in different jurisdictions. For example, the US Federal Court dismissed a lawsuit against Valve because of loot boxes in CS:GO — loot boxes in the game were not recognized as an element of gambling. Also on March 9, 2022, the Supreme Administrative Court of the Netherlands overturned the decision of the court of first instance, which obliged EA to pay € 10 million for the implementation of loot boxes in FIFA. Conversely, in March 2023, the Austrian Court in the Hermagor district ruled in favor of several Austrian players who sued Sony in 2020 – the FIFA loot boxes in the PlayStation version were recognized as an element of gambling.
6. The owners of the Russian legal entity Game Insight are suspected of deliberate bankruptcy
In June 2022, Game Insight left the Russian market due to the sanctions policy. The assets of the Russian company were transferred to the new management. However, in August 2022, an application for declaring the company bankrupt was filed with the Moscow Arbitration Court from the Russian Game Insight LLC. The company was declared bankrupt in October 2022. The amount of unfulfilled obligations at that time was 76.2 million rubles, of which 66.5 million rubles were non—payments to employees on wages and severance payments.
According to the information of the arbitration management company, the Lithuanian Game Insight did not pay more than € 1.4 million to the Russian legal entity, citing the impossibility of conducting operations due to sanctions. However, according to the arbitration manager, both companies were de facto controlled by the same group of persons. The arbitration manager believes that the bankruptcy of the Russian “Game Insight” was intentional: the Lithuanian company could fulfill monetary obligations, despite the sanctions restrictions.
The arbitration manager appealed to the prosecutor’s office in order to bring the persons controlling the company to justice. The status of consideration of the appeal is still unknown.
On February 21, 2023, the Russian Game Insight filed a claim for recovery of the amount owed to the Lithuanian Game Insight in the Arbitration Court of Moscow. The hearing on the case is scheduled for July 18, 2023.
Recall that the Russian “Game Insight” refused to pay salaries for the last month and severance payments to its employees, contrary to the requirements of labor legislation. Four years earlier, based on information in the media, the chairman of the board of directors of Game Insight Igor Matsanyuk did not pay a “large” amount of money to the former president of the company Maxim Donskikh at his dismissal. It is not known about the appeal to the court with the relevant claims of Maxim Donskikh.
7. Astrum Entertainment and MY.GAMES have agreed on the Warface section
In December 2022, the game publisher MY.GAMES announced its withdrawal from the Russian market. Four months later, he signed an agreement with Astrum Entertainment regarding the Warface shooter. This is one of the most famous projects of MY.GAMES, which has earned more than $700 million over 11 years. Most of the Warface audience is made up of Russian gamers.
Under the terms of the deal, Astrum reserves the current version of the game, its Russian audience and brand. The development of the project will be limited to the territory of the local market. MY.GAMES has retained the source code of the game, on the basis of which it will launch a new project abroad. Warface in Russia will be developed through VK Play, and the international version of the shooter will be available on Steam and Epic Games Store.
Restarting Warface may be limited to the usual repackaging of the brand, as well as a global reworking of game mechanics, which implies significant investments. According to media reports, the transfer of the source code could cost MY.GAMES $ 100-150 million, but the company insists on the gratuitousness of the transaction.
8. The organizer of the exhibitions Comic Sop Russia and IgroMir may be declared bankrupt
KRI LLC is the organizer of the exhibitions Comic Con Russia and IgroMir, which is the copyright holder of the corresponding trademarks. In 2021, due to covid restrictions, the company canceled the IgroMir exhibition, one of the participants of which was the manufacturer of computer peripherals LLC DIS-3. In April 2021, DIS-3 paid the participation fee to KRI, but it did not return this money to DIS-3 upon the cancellation of the exhibition. After that, DIS-3 appealed to the Moscow Arbitration Court with a claim for the recovery of 3.5 million rubles. His claim was granted.
“KRI” did not fulfill the awarded requirements. In this regard, in December 2022, DIS-3 appealed to the Moscow Arbitration Court with a demand to declare KRI bankrupt. Based on publicly available information, other creditors have joined the bankruptcy procedure of the company.
According to media reports, at the beginning of 2022, the purchase of “KRI” was considered by MTS, but it refused the deal after the departure of foreign brands from Russia. According to rumors, the shareholders of KRI intend to curtail their activities in Russia, since foreign companies probably will not participate in the exhibition now.
At the time of writing, KRI was not declared bankrupt, a monitoring procedure was introduced against the company. The next bankruptcy hearing will be held on June 21.
9. A special version of PUBG: Mobile has been unlocked in India
In the previous digest, we wrote about the blocking of the Battlegrounds Mobile India game in India — the Indian version of PUBG Mobile. On July 29, 2022, the government of India banned the game for reasons of national security. It was alleged that its developer Krafton transferred the personal data of Indian players to servers located in China.
On May 18, 2023, Krafton announced on the official website of the game that it had received permission from the Government of India to re-launch Battlegrounds Mobile India. According to the information provided by Krafton, the company has eliminated the identified violations and has taken measures to protect the personal data of players in accordance with the laws of India. The developer has not announced any significant changes to the mechanics of the game. We believe that the changes only affected the logistics of collecting and processing personal data.
Note that Battlegrounds Mobile India has been returned to India for only three months so far. During this period, the country’s authorities will monitor whether the game complies with local legislation.
10. A class action lawsuit against Nintendo over the marriage of Joy-Con sticks was dismissed
In 2020, a class action lawsuit was filed against Nintendo due to the drift of Joy-Con sticks: the plaintiffs were two women who purchased a Nintendo Switch portable console for their children.
It is reported that Joy-Con sticks often failed among consumers: at first, the sticks spontaneously “drift”, then this defect only worsens and leads to a complete malfunction of the controllers. This forces you to purchase a new pair of sticks. Nintendo was accused of deliberately implementing sticks, the design defect of which was initially known.
A study by the British consumer group “Which?” testifies to the shortcomings of the design of Joy-Con sticks, which caused mechanical malfunctions that cause the same drift.
The District Court of California rejected the class action because Switch comes with a license agreement that de facto restricts the ability of the end user to make claims against the company in court. We assume that the court considered the parents’ argument about the impossibility of restricting the rights of minors by a license agreement untenable.
Note that back in 2020, Nintendo President Shuntaro Furukawa apologized to Switch users for the inconvenience caused by problems with Joy-Con sticks.
11.Epic Games’ appeal against Apple has been reviewed: the lower court’s decision is upheld
On April 24, 2023, the U.S. Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals sided with Apple in the infamous dispute with Epic Games, the developer of Fortnite. The decision of the lower court was upheld. He confirmed that Apple is not a monopolist within the meaning of the current antimonopoly legislation. However, the Appeals Board recognized the decision of the court of first instance as completely legitimate and in the part in which Apple was obliged to allow third-party developers to add links to third-party payment systems to applications. At the same time, Epic Games is obliged to compensate Apple’s legal costs, as well as to compensate damages for bypassing the App Store‘s internal purchase system.
The Court of Appeal did not agree with the arguments of Epic Games about the improper application of antitrust laws by the judge. In the appeal, Epic Games argued that Apple artificially restricts the possibility of implementing payment systems, and that Apple denies developers access to iOS if they do not use Apple’s payment system in applications.
Recall that the conflict between Epic Games and Apple began in 2020, when Epic Games added the ability to purchase in-game currency outside the App Store to Fortnite, and Apple’s response was to remove the game from the app store. Apple was accused of a monopoly in the field of applications and payment systems on iOS. Epic Games was supported by both government agencies represented by the US Attorney General’s Office and technical companies up to Microsoft. Epic Games was also supported by 35 US states.
In early June, both companies filed new appeals.