What is the average salary of game developers in the market, how many of them are women, does higher education affect wages — these and many other questions are answered by a new salary study from Talents In Games and App2Top.ru .
Methodology
From October to December 2020, a survey of Russian-speaking game developers was conducted through a Google form. The link to the survey form was distributed via App2Top.ru and a number of specialized groups on social networks. Based on the responses received, the results presented below were prepared. In the part devoted to salaries, only median values are indicated.
General information on the study
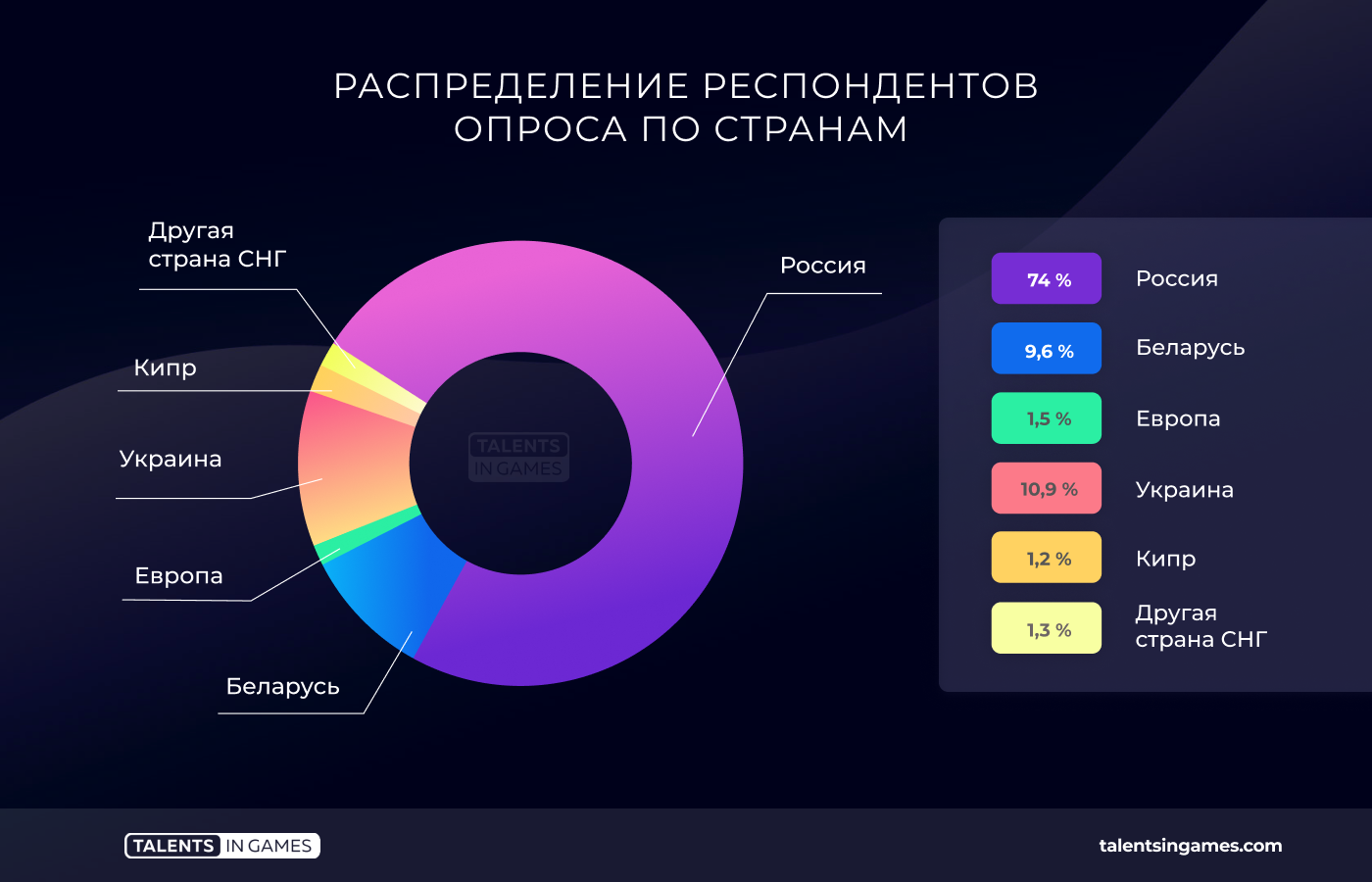
1,379 people participated in the survey. Most of the respondents work in Russia (74% or 1,021 people). There were also enough representatives of Ukraine (10.9% or 150 people) and Belarus (9.6% or 133 people) among the respondents.
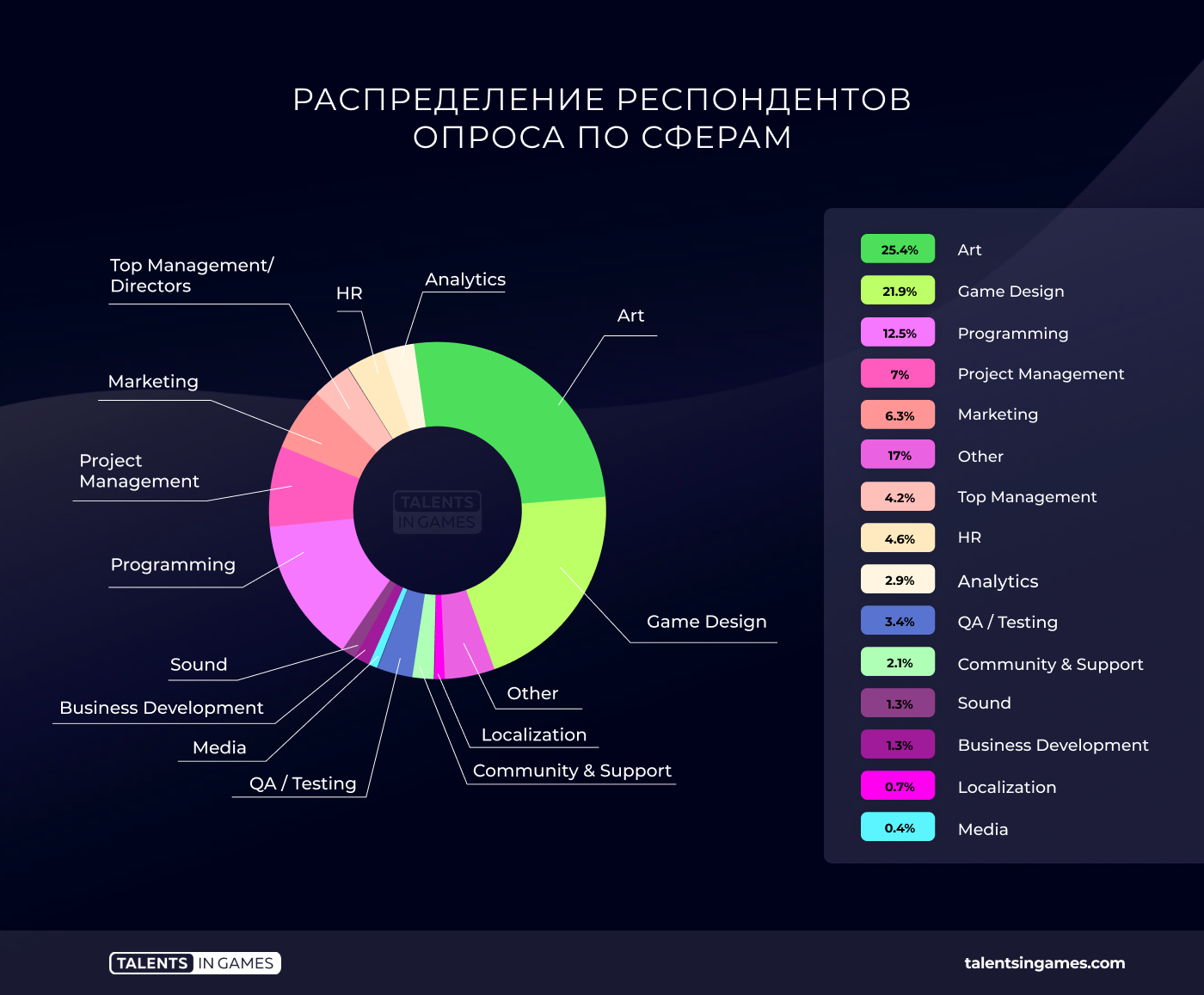
The survey has the most responses from artists (25.4%), game designers (21.9%) and programmers (12.5%).
Part One: Gender, age, education, seniority and English as salary factors
Gender of developers
The gaming industry in the CIS remains predominantly male. There are only 34.1% of women in the industry.
The ratio strongly depends on a particular specialty. For example, there are only 8% of them among game programmers. The absolute majority of the top management of gaming companies in Russia, Belarus and Ukraine — 87.9% — are also men.
Equal representation of men and women can be said only within the framework of several gaming professions. Among artists, women account for 47%, and among business development specialists, they account for 44.4%.
Women prevail only in two directions, not counting finances and office work. It’s about HR and PR. In the first, women account for 95.2%, in the second — 83%.
As for the median salary, it is usually 25% less for women throughout the Russian-speaking gaming industry than for men (for example, a female programmer, with general equals, according to data, receives less than a female artist).
Age of developers
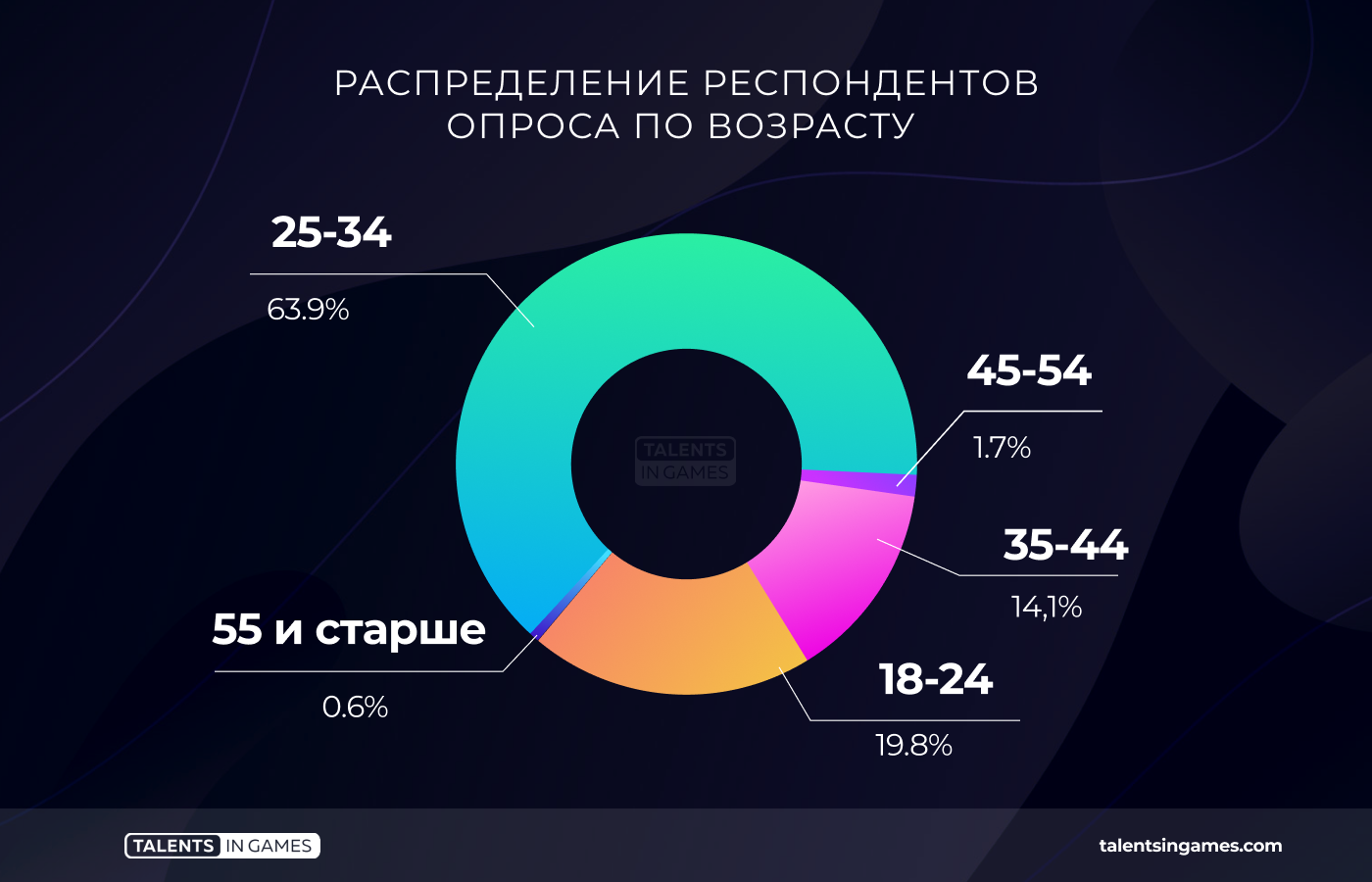
Only 19.8% of developers are under 25 years old. Mostly people from 25 to 34 years old work in the industry (63.9%). There are very few conditional “veterans” who are over 45 years old — just over 2%.
In general, this ratio is true for the main specialties (programmers, artists, game designers). The percentages may vary, but only slightly.
However, there are exceptions:
- there are significantly more people over 35 among top managers than in the industry as a whole. The share of people aged 35 to 44 in this field reaches 31%. About 7% of the tops are over 45 years old. But there are almost no young people (3.4%);
- the situation is somewhat similar with gaming HR specialists. The proportion of young people (under 24) is quite small (11.1%). At the same time, there are a lot of personnel from 25 to 34 years old (70%). 6.4% of representatives of the profession are over 45 years old;
- business development specialists are represented by only two age groups. From 25 to 34 years (55.6%) and from 35 to 44 years (44.4%);
- community and support specialists are mainly people from 25 to 34 years old. There are very few of them (at the level of 10%) and those who are younger and those who are older.
Out of curiosity. The number of analysts among people over the age of 34 is small. 82.5% of specialists in this field are still very far from 40 years old. There are no people over 45 here at all.
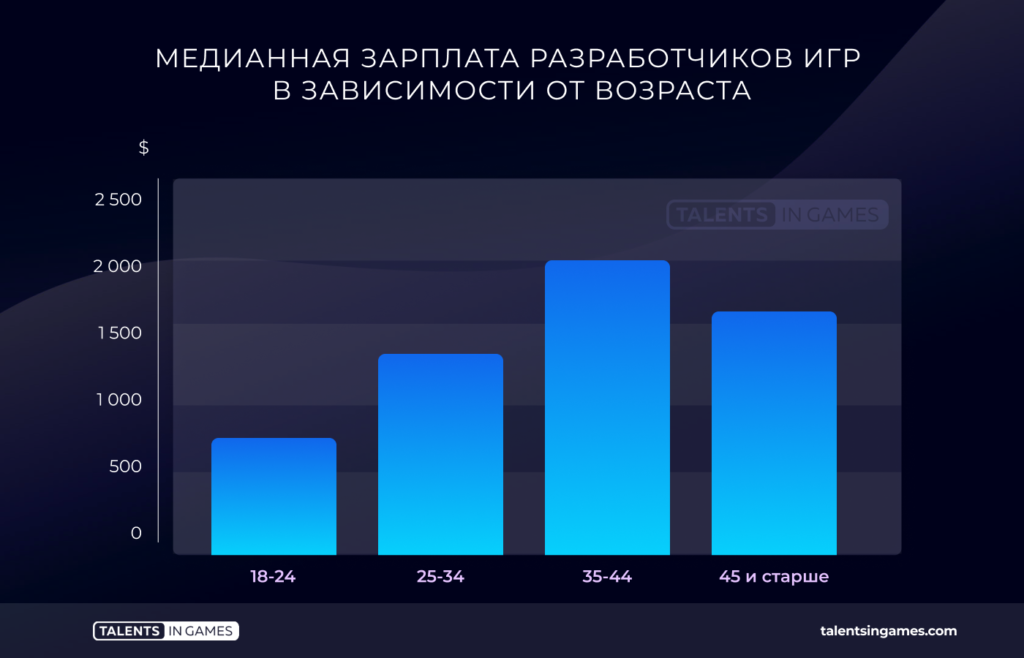
There is a statistical dependence of the median salary on age. The peak salary is received by specialists from 35 to 44 years old.
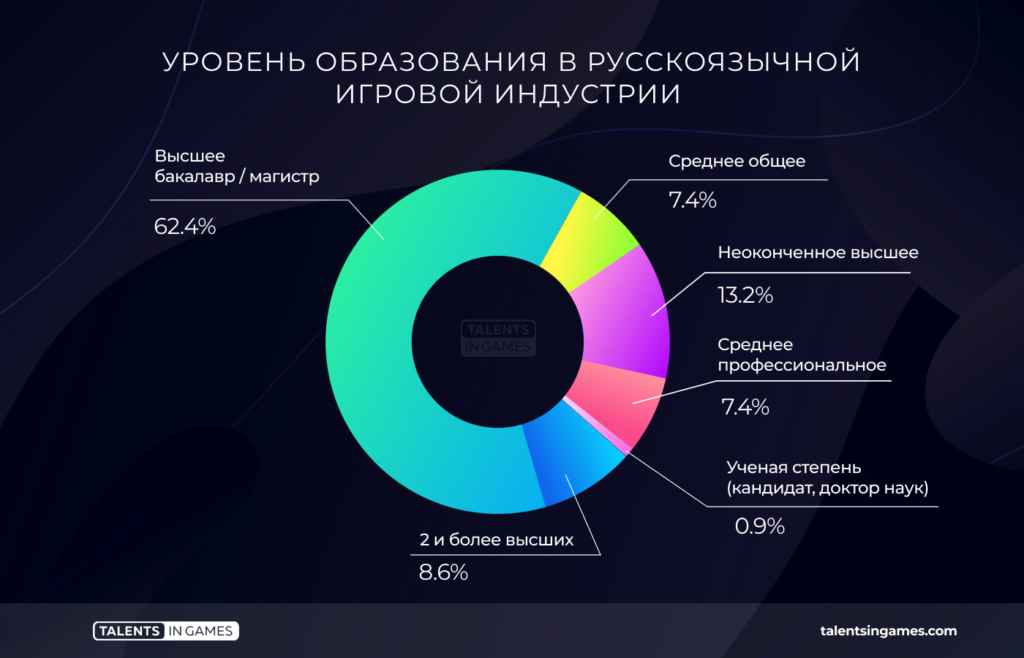
Education
71.9% of respondents have completed higher education. With minor changes, this is true for every game slice. For example, among programmers, people with higher education are the same 71%.
Stand out against the general background:
- support specialists: only 62.1% of the staff have completed higher education;
- artists: the share of diploma holders is also noticeably lower among them — 63.7%;
- top managers: among them there are more people who graduated from universities — 84.4% (and that’s not all, 17.2% have more than two higher ones);
- analysts: 85% of them have a higher education (moreover, 7.5% have an academic degree);
- marketers: 86.2% have a higher education;
- localizers: 88% have a higher education;
- business development specialists: among them, the share of people with higher education is the highest — 95%.
The advantage is higher where knowledge is needed for work, which can only be obtained at a sufficient level in higher educational institutions. The exception is tops that require higher education to increase and maintain expertise.
There is no direct relationship between the level of education and salary, but there is an obvious correlation: the higher it is, the larger the median salary.
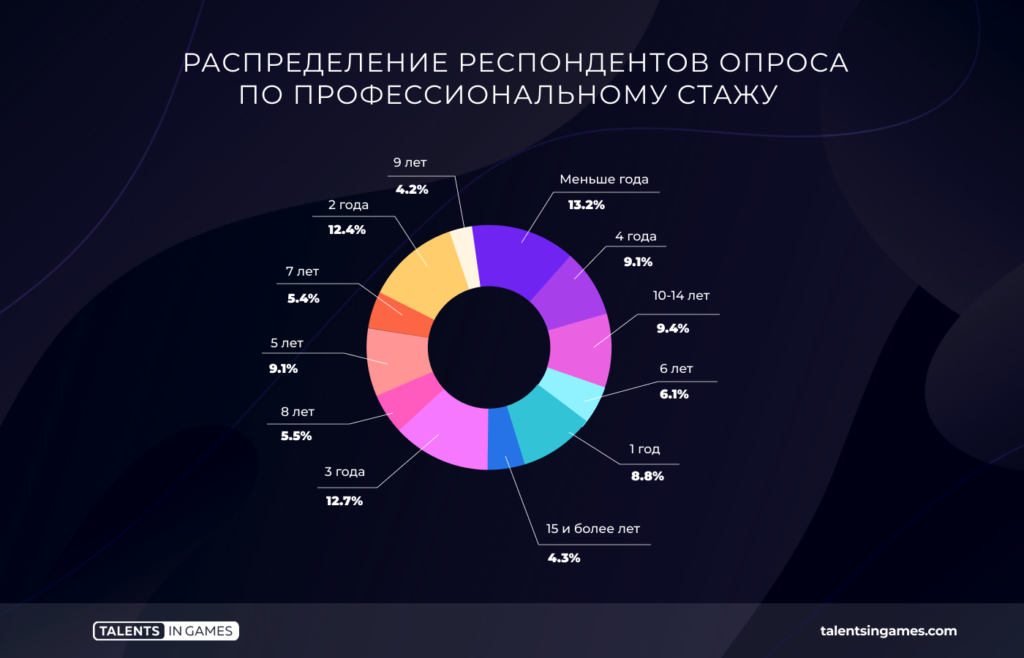
Professional experience
Specialists with completely different professional experience took part in the survey. There is no unambiguously dominant group. Maybe a little more people with less than a year of experience and people with three years of experience.
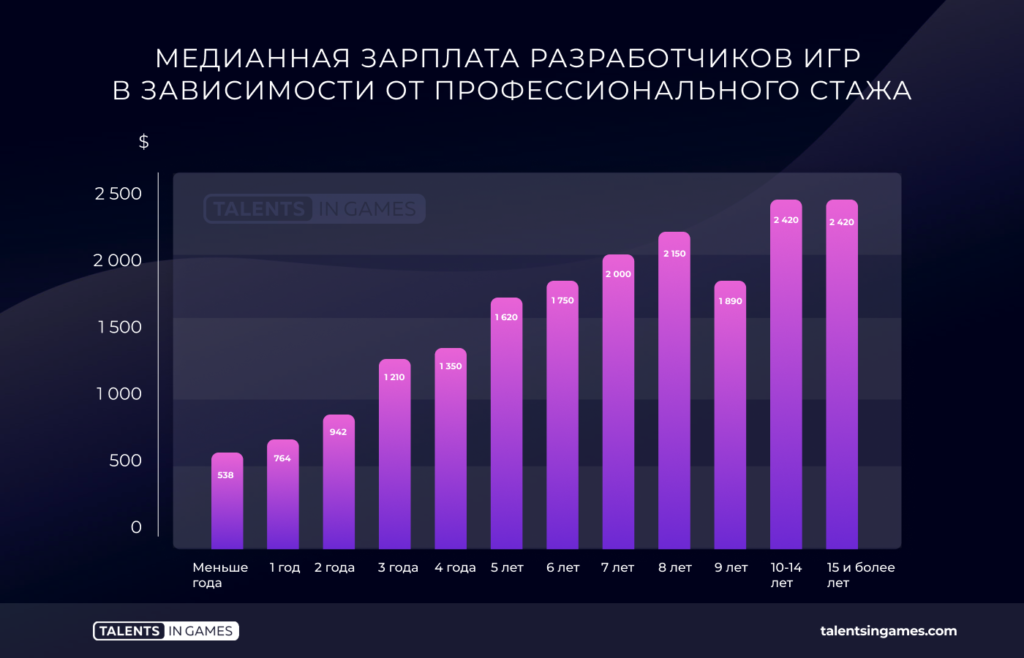
There is a correlation between the amount of professional experience and the median salary. The more a person works, the higher the rate. However, there are slight fluctuations in the interval between seven and nine years. And it’s fair to say that the median salary of a gaming specialist with 7-9 years of experience remains at $2,000. At the same time, the median fee of the “veterans” of the game dev is already about $ 2,400.
Experience in the company
The situation with the experience at the current place of work indicates a high turnover of personnel in the labor market. A large proportion of respondents — 39.4% — changed jobs less than a year ago, and another 18.4% have been working for about a year.
Only 16.2% of the gaming industry employees have been working within their current company for 4 years or more.
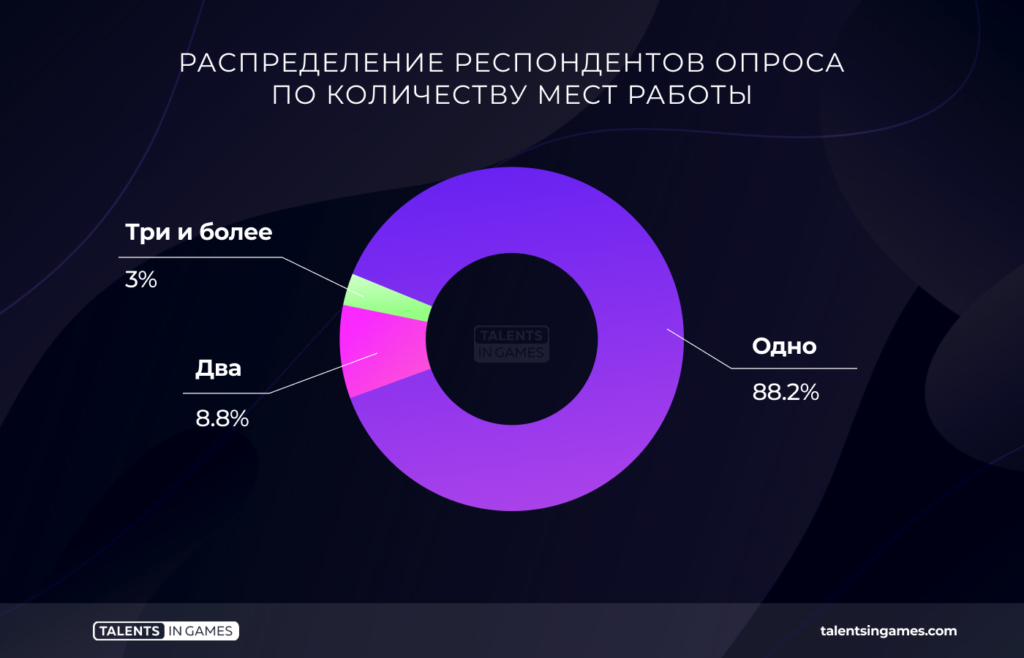
Number of paid jobs
The majority of respondents work at the same job (88.2%). The share of specialists employed in several companies is small. Although the option with two jobs can hardly be called exceptionally rare (8.8%).
This situation is true for the entire industry. Only localizers are seriously out of the picture. 22.2% of them work in two places at once, and 11.1% work in three places at all.
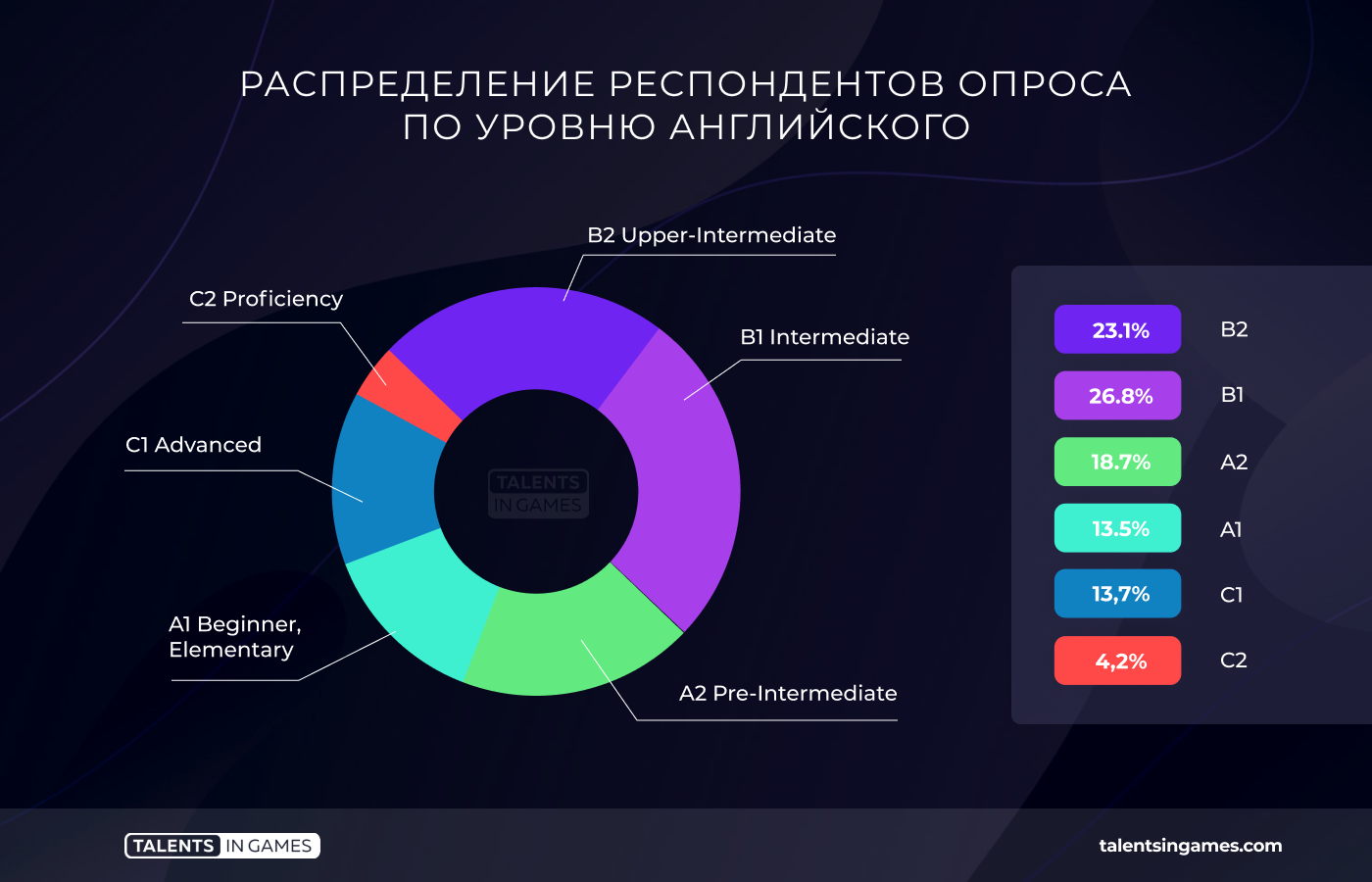
English level and its impact on salary
Knowledge of English in the industry leaves much to be desired. Only 41% of respondents have English at the Upper-Intermediate (B2) level, which is necessary for communication on professional topics, and higher.
There is a direct correlation between the level of English and the median salary. The higher the language proficiency in a group, the higher the salary of this group. Fluency in English (C2 Proficiency) by itself is unlikely to provide a high salary, but it can contribute to this.
At the same time, 67.3% of respondents noted that they use English at work. This also indicates the high demand for English in the industry.
Part Two: Gaming specialties and salary
Median salary for the entire Russian-speaking segment
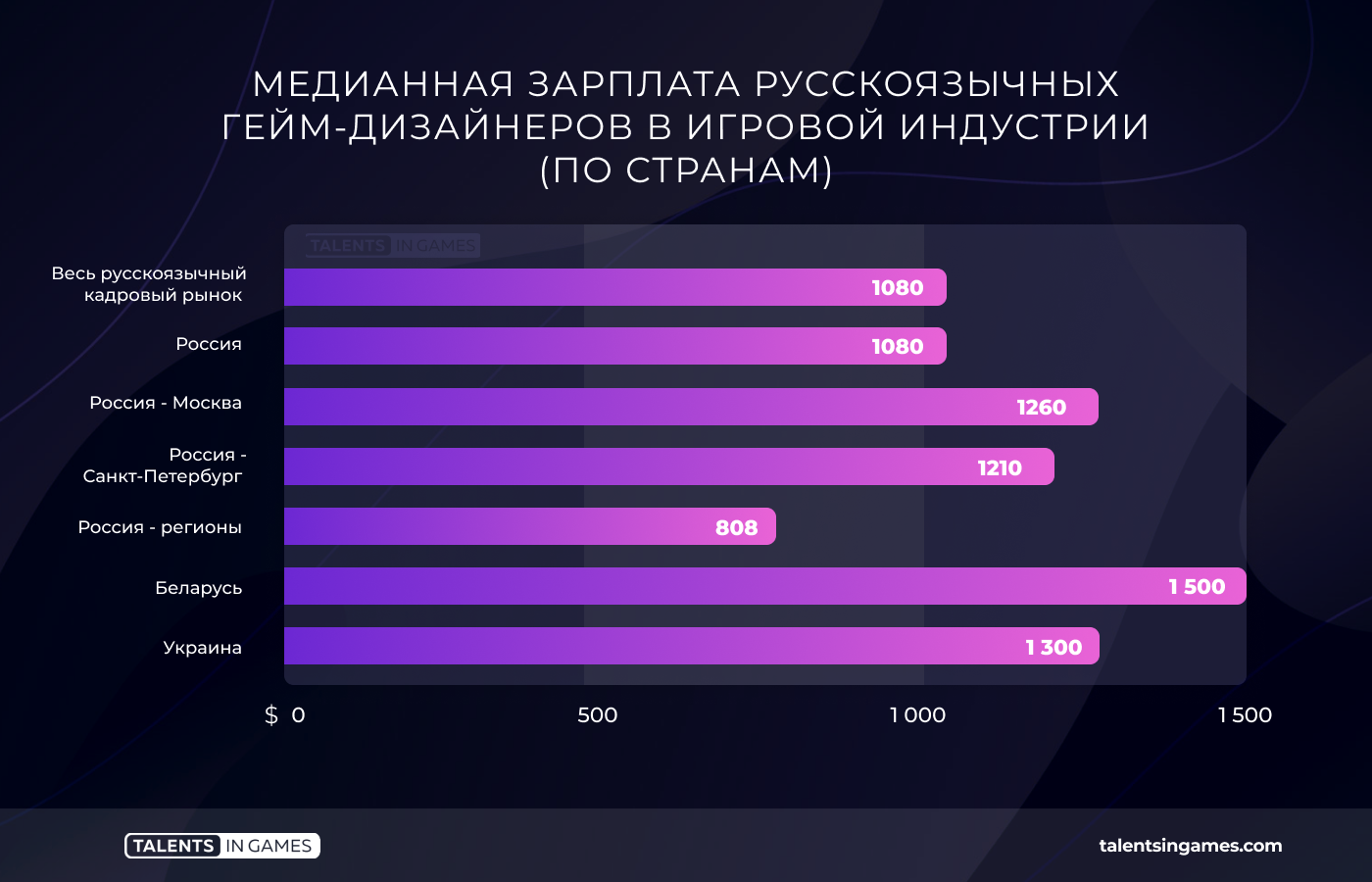
The median salary for the entire Russian-speaking industry is $1,211. It strongly depends on both the country and the city.
For example, in Russia, the median salary in the country is the lowest. It is $1,080. At the same time, it is much smaller in the regions.
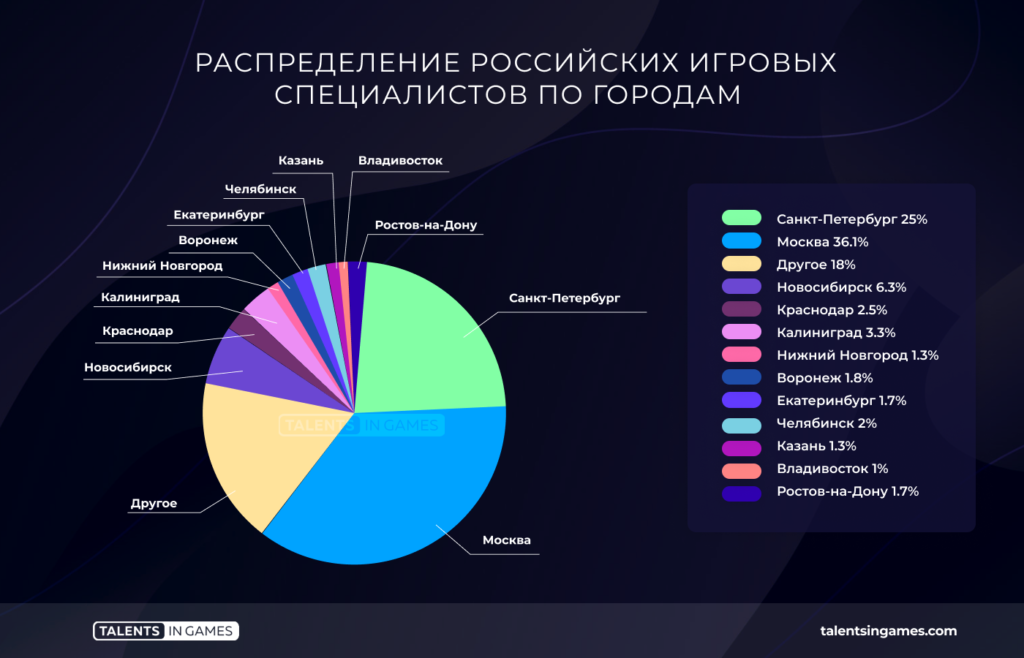
The Russian development cannot be called significantly distributed. The majority (61.1%) of the personnel work from the capitals — Moscow and St. Petersburg. The industrial “hubs” of other cities are much smaller than them.
The median salary of a gaming specialist throughout Belarus is higher — $1,500. At the same time, it is also the median for Minsk. But in the regions of Belarus, the median is at $600, but here it is important to make two clarifications: 94% of the Belarusian industry is concentrated in the capital, and the number of responses from regional specialists was quite small for a representative sample (around a dozen).
As for Ukraine, the median salary in the country is also $1,500. The same in Kiev. However, in the regions it is at the level of $ 1400. Plus, an important difference from Belarus is the significant distribution of the gaming sector across the country. 24.7% of specialists work in Kharkiv, and almost 7% more work in Lviv.
Programmers (174 questionnaires)
The median salary of a game programmer across the region is $1,620. In general, it is less in Russia than in Belarus or Ukraine.
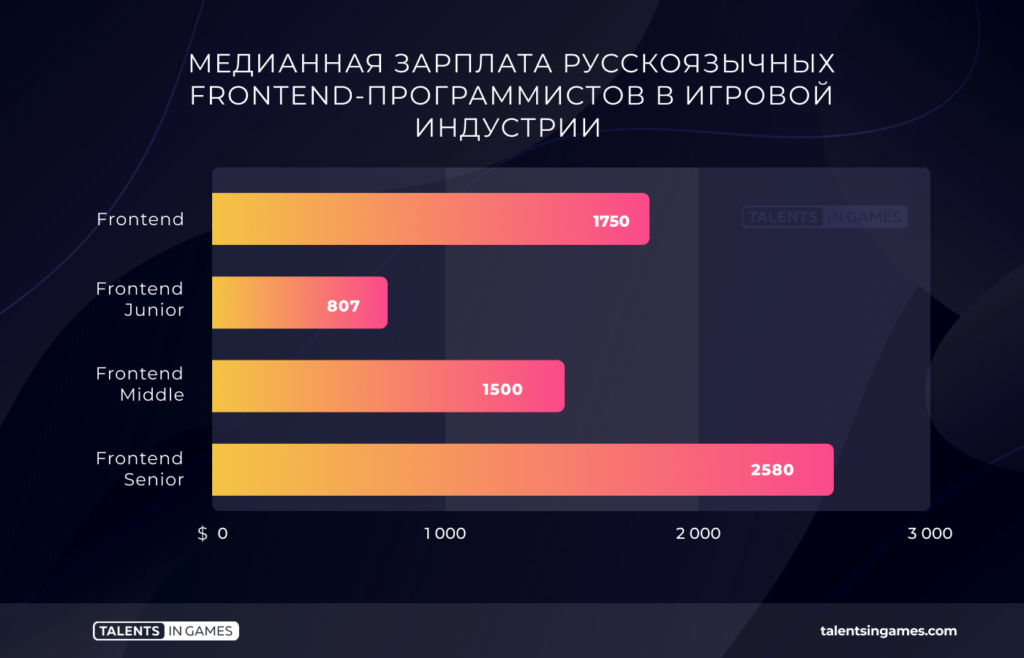
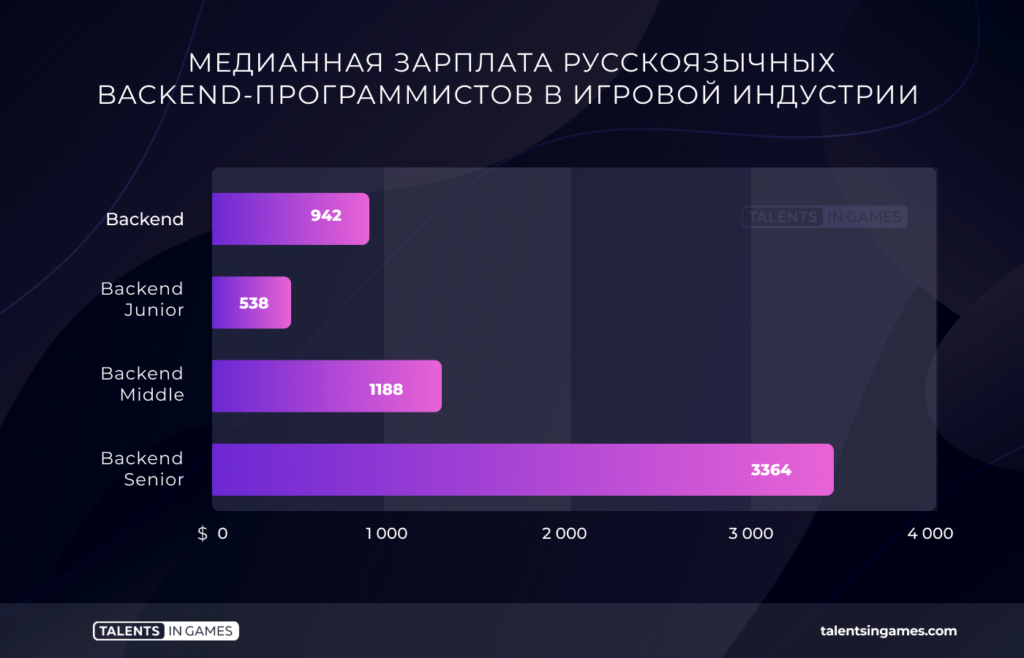
The highest median rate is for Frontend specialists. Plus, they get more at each level (junior, middle, and so on) than their colleagues.
Backend programmers lag behind them in terms of the median salary, but in a particular study, the skew occurred due to the large number of Backend juniors who took part in the study.
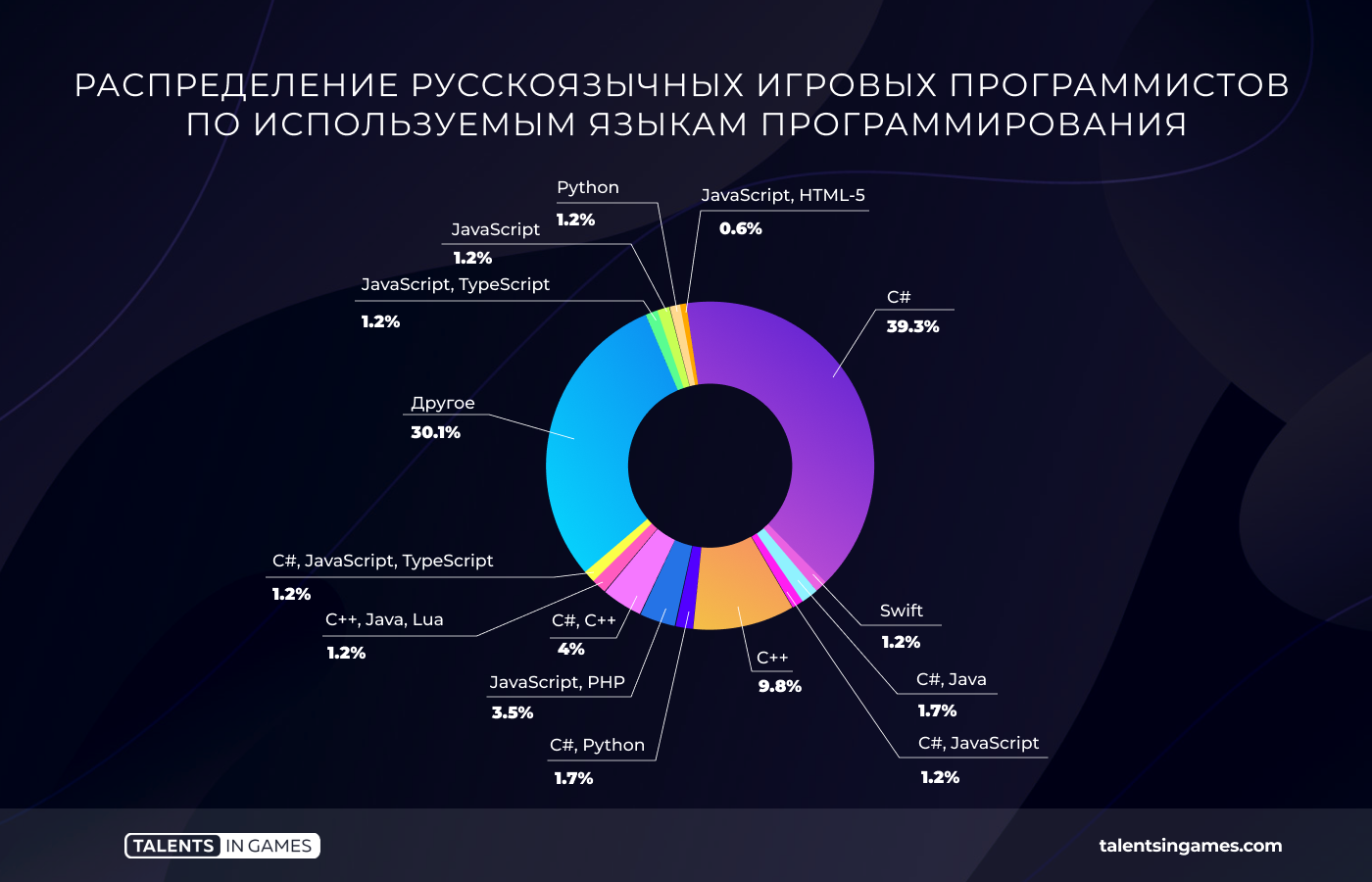
Most of the surveyed game developers use C# in their work. But at the same time, 39.3% of respondents write exclusively on “sharp”. The second most popular language is C++. 9.8% of the surveyed specialists are engaged in coding on it.
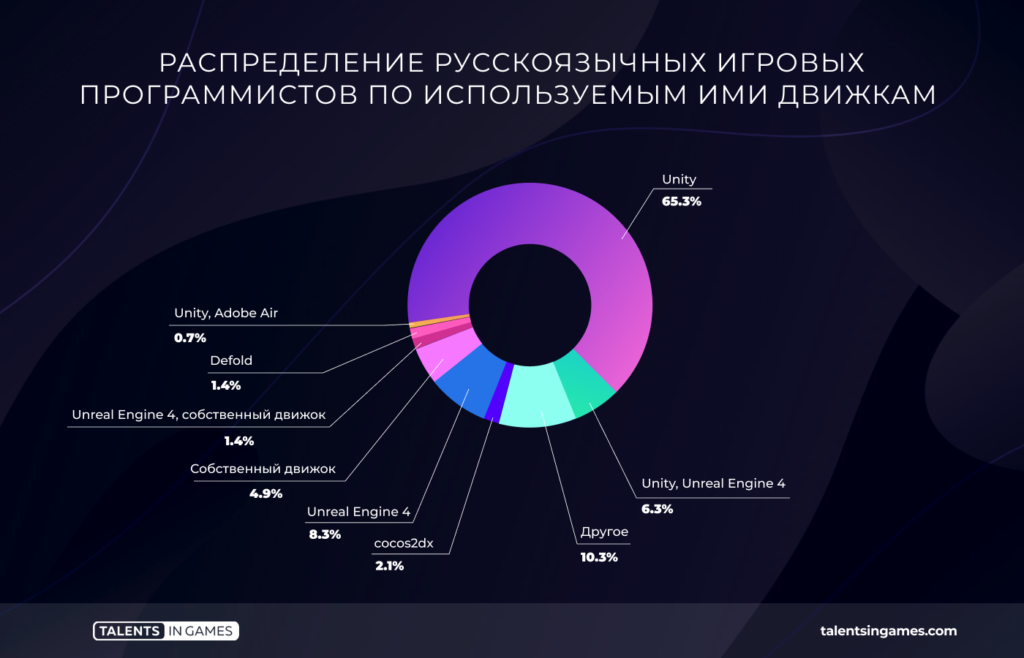
Given the prevalence of C#, it is not surprising that Unity turned out to be the main engine for most of the respondents (65.3%). Unreal Engine is in second place by a huge margin (8.3%).
At the same time, now the median salary of a programmer working with Unreal is higher. It is $2024. The median rate of a Unity programmer is $1400.
Also note:
- 54.8% of programmers stated that their desired salary level is $3000;
- 92% of programmers in the games industry are men;
- a quarter of programmers employed in game development are under 25 years old;
- 71.1% of programmers have a higher education.
Artists (351 questionnaires)
Across the entire market, the median salary of an artist in the CIS is $942. The same number in Russia. In Belarus, it is slightly less. However, in Ukraine, where many work for outsourcing to Western companies, the median is more — $1,230.
The salary of 2D artists ranges from $300 to $2500 per month. However, the median for the market is closer to the lower value. It is $700. However, Senior-level specialists can safely count on more than $1300.
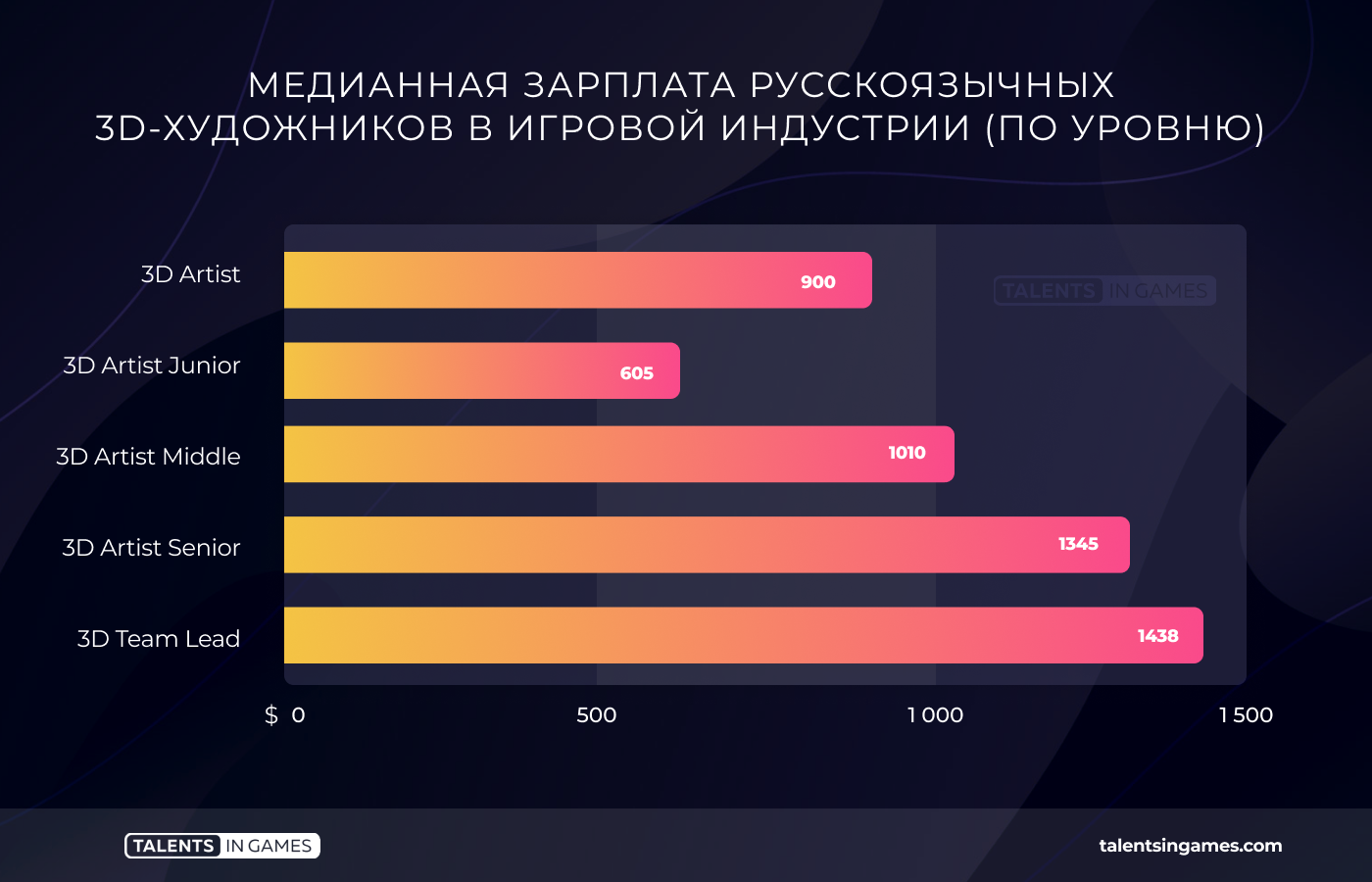
3D artists get more than 2D. Their median salary hovers at $900. At the same time, middle specialists receive more than $1010 in half of the cases. The peak salary for a three—dimensional “middle” is $1600. Only the rates of more experienced and professional personnel are higher.
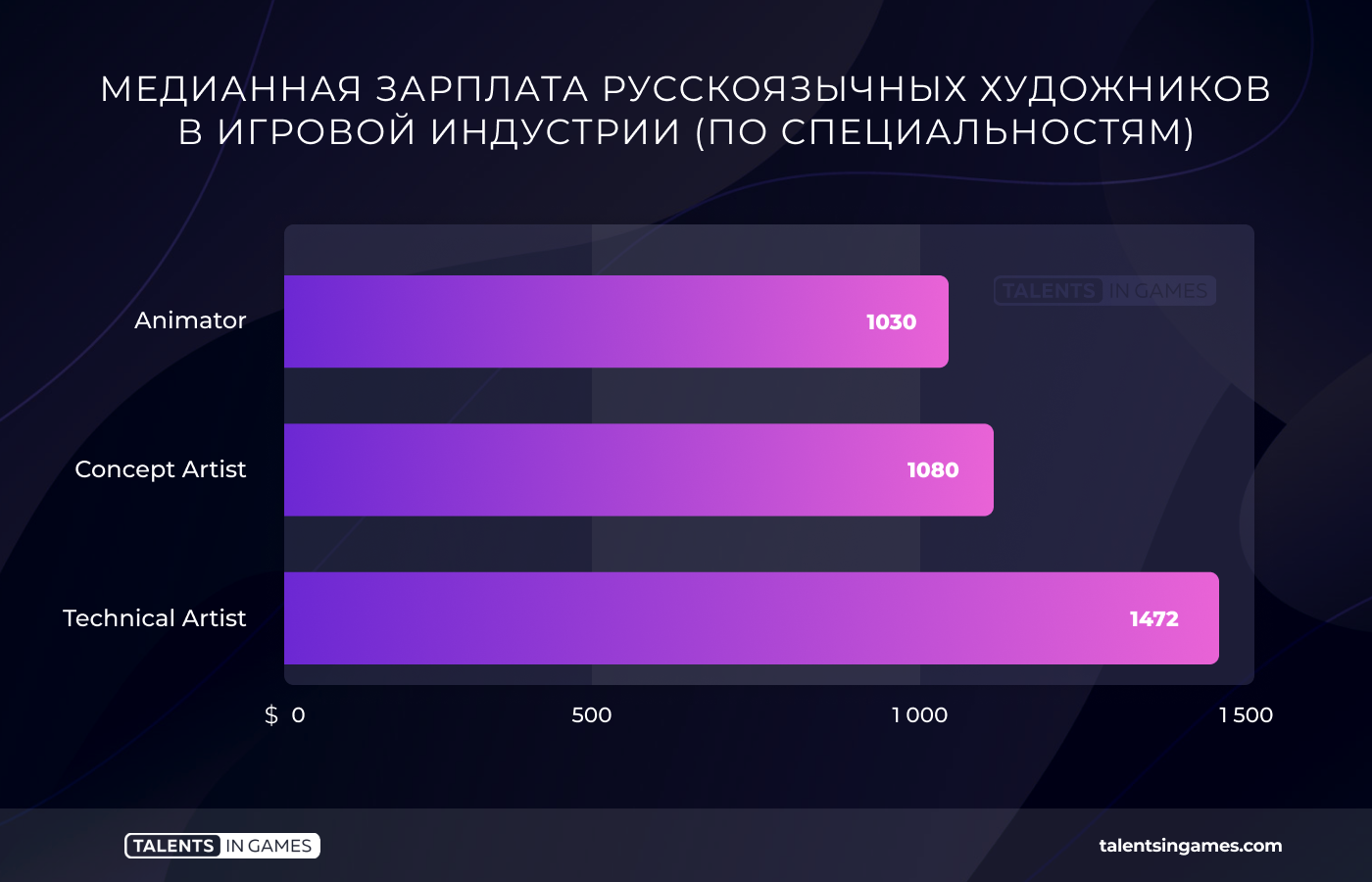
Salaries of animators and concept artists are about the same level. But the salary of technical artists in our survey turned out to be significantly higher than theirs, amounting to almost one and a half thousand dollars.
The salaries of graphic designers differ slightly from the salaries of two-dimensional artists. The median rates of ordinary specialists in 50% of cases do not reach $ 1000, as for leads, they can count on $ 1500.
The situation is quite different with interface artists and graphic effects specialists. The median salary of both the first and second is several hundred dollars higher. As for the leading artists in these fields, half of them earn more than $2,000 a month.
The latter receive at the level of an art producer, whose median salary, according to the survey, is $2,153.
Also note:
- 42% of artists said they would like a salary of $1800;
- 47% of game artists are women;
- 16% of game artists noted that they work in several places;
- only 63.7% of artists have completed higher education.
Game designers (303 questionnaires)
Game designers have the highest median salary in Belarus. There it is $1,500. Also, relative to the entire Russian-speaking region, Ukraine has a fairly high salary with a rate of $ 1300. This is about the same as in Russian capitals. As for the Russian region, the median in the whole country does not even reach a thousand dollars.
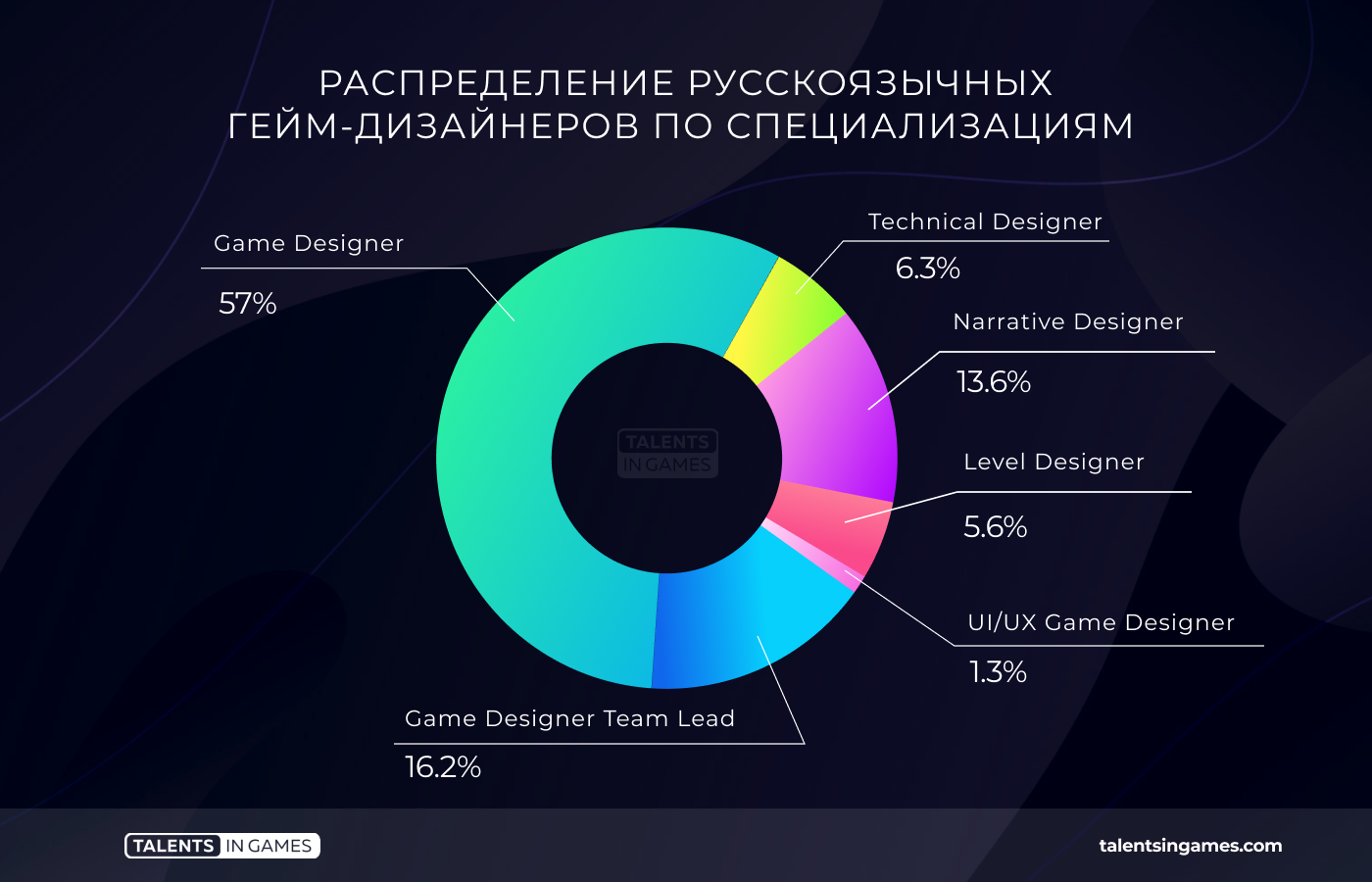
In the study, game designers were segmented into generalists (Game Designers), narrative designers (Narrative Designers), Level Designers (Level Designers), technical designers (Technical Designers) and UI/UX designers (it is important not to confuse here).
Most of all it turned out to be game designers of a wide profile (57%), which is expected. As a rule, our specialists in this profession solve numerous tasks of completely different kinds. Specialization exclusively on some particular function (for example, on level design) is more typical of large corporate giants, of which there are not so many in the Russian-speaking market.
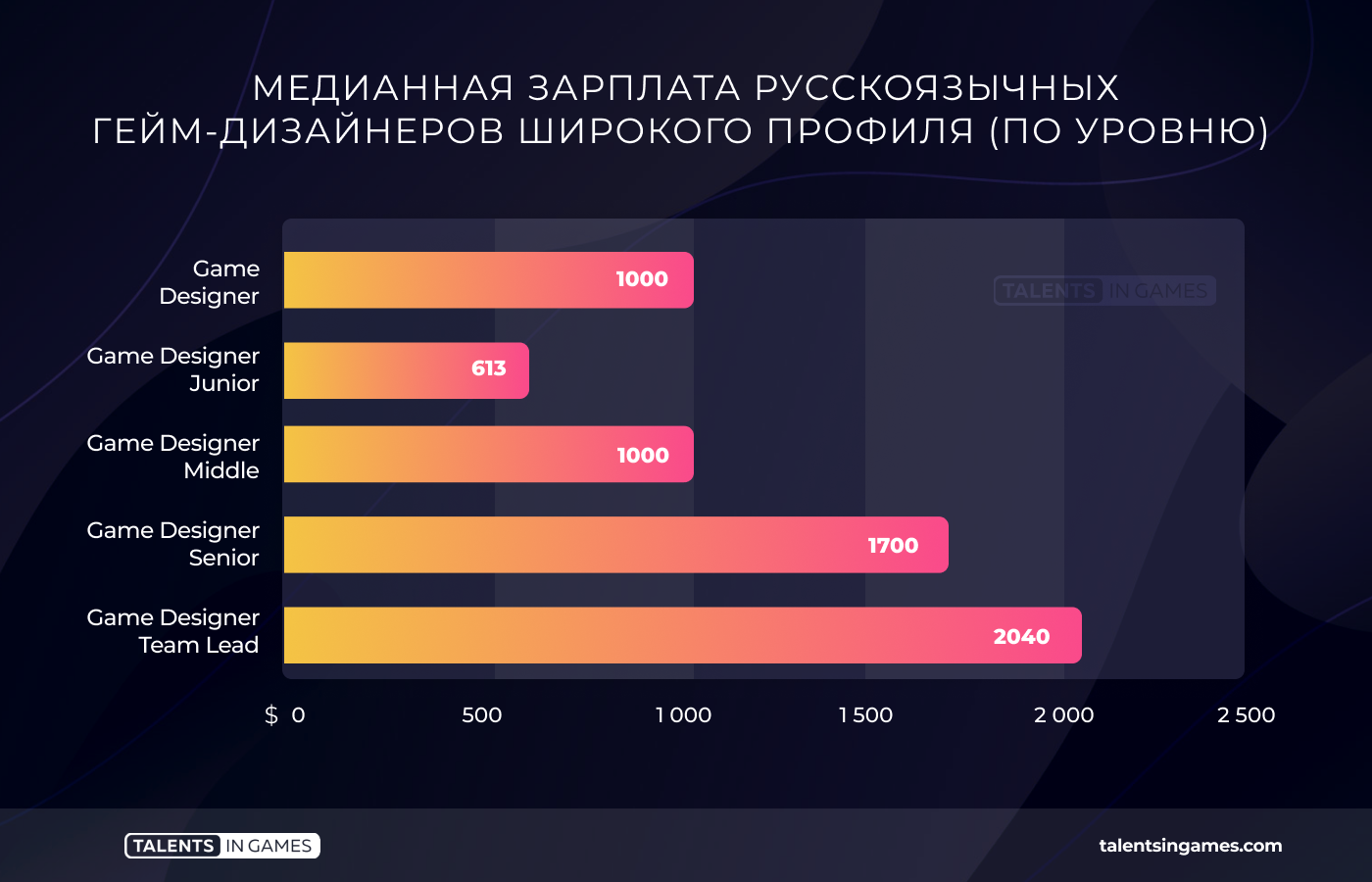
A novice general-profile game designer in half of the cases cannot count on a salary above $ 613. At the same time, the median salary of the head of the game design team is already a significant $2040.
The difference in earnings between narrative specialists, which also often include screenwriters, of various levels is not so significant. If the median salary for a beginner is $915, then the “senior” has only $1211.
There is no big difference in wages between specializations. In general, the median salary of an average game designer, regardless of the profile, is about a thousand dollars. The only exception is the UI and UX designer. He gets more than $1400 in 50% of cases.
Also note:
- 73% of game designers are men;
- more than 60% of specialists in this field are people from 25 to 34 years old;
- 69.4% of game designers have a higher education.
Top managers (59 questionnaires)
The most affluent group of respondents. In the responses, some indicated the amount of monthly earnings in the region of $ 40-60 thousand per month. About ten people indicated that their salary is $ 12-18 thousand. At the same time, the median for the Russian—speaking market is around $ 4,000.
It is important to understand here that top managers meant both directors and heads of directions, as well as founders of companies, as well as general producers.
Despite the fundamentally different positions, there was not a very large spread in median salaries between them. It is worth highlighting only that CEOs and marketing directors receive more on average, while game design directors and development heads receive less.
Note:
- 37.9% of top managers are over 34 years old, in other words, this is one of the most “age” groups in the industry;
- among the tops, the percentage of women is very small — only 12.1%;
- also among them is the highest percentage of people with two or more educations in the industry (17.2%).
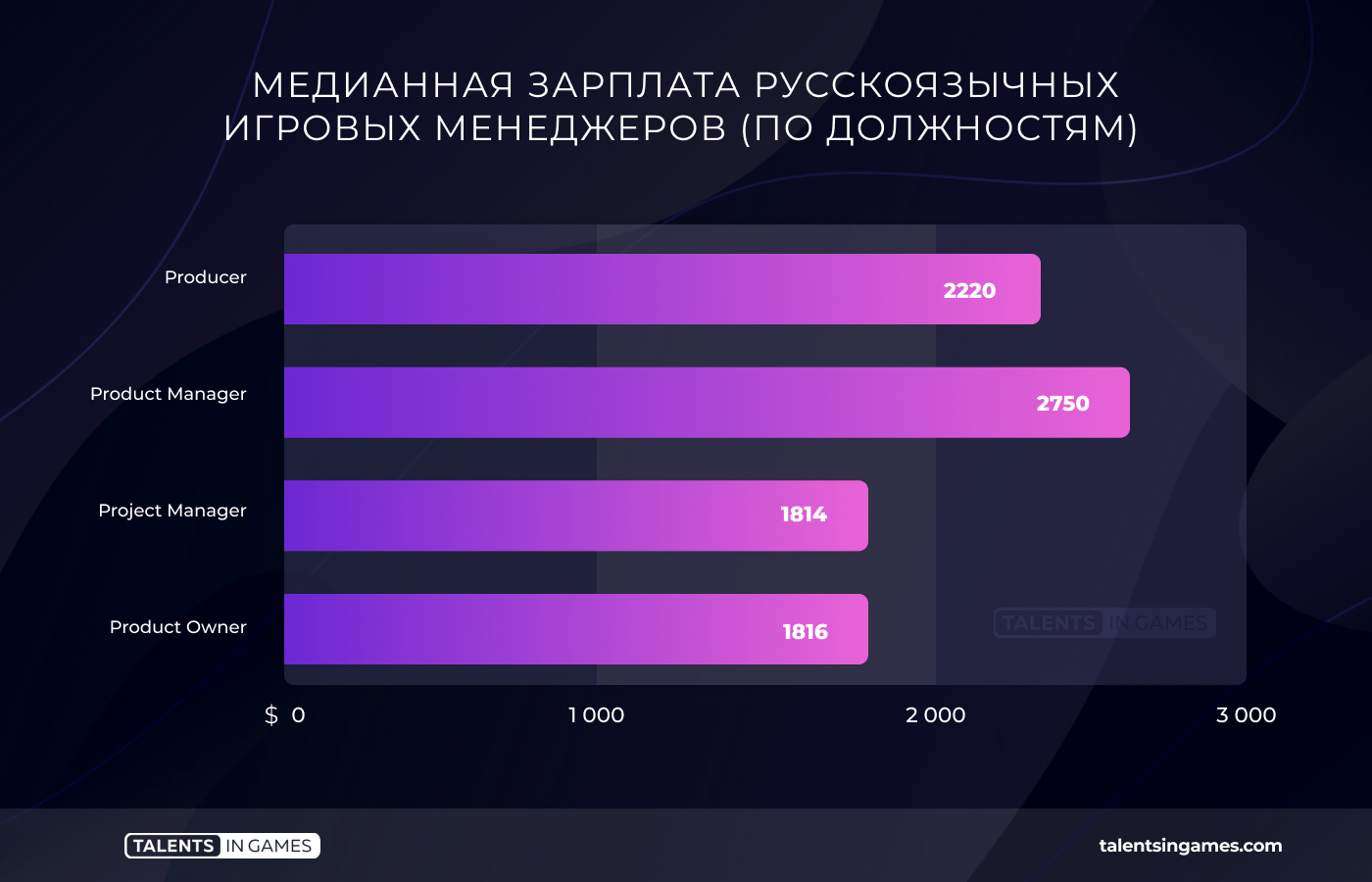
Middle managers (97 questionnaires)
The median salary of middle managers is $2020. As in other cases, the lowest median salary for specialists in this profile is in Russia (especially in the regions). The highest is in Belarus, where in half of the cases it is above $3,000.
The largest number of responses were received from project managers and producers, so the data on them are the most representative. As for product managers and product managers, we have collected a dozen questionnaires from them. This is a sufficient figure, but in accuracy it is, of course, inferior to the data for the groups mentioned above.
Taking into account all the above, we note that, in general, managers of the average middle level today in the CIS can safely count on a salary of $ 1,800-2,200, depending on specialization. Although, according to the collected data, there are exceptions. Some specialists receive both $6000 and $7000. At the same time, the lower threshold is $500-600.
Note:
- 70.8% of middle managers are men;
- 69.8% of the frames in this segment belong to the age group of 25-34 years;
- 15.6% of managers have two or more higher educations (75% have a diploma of completed higher education).
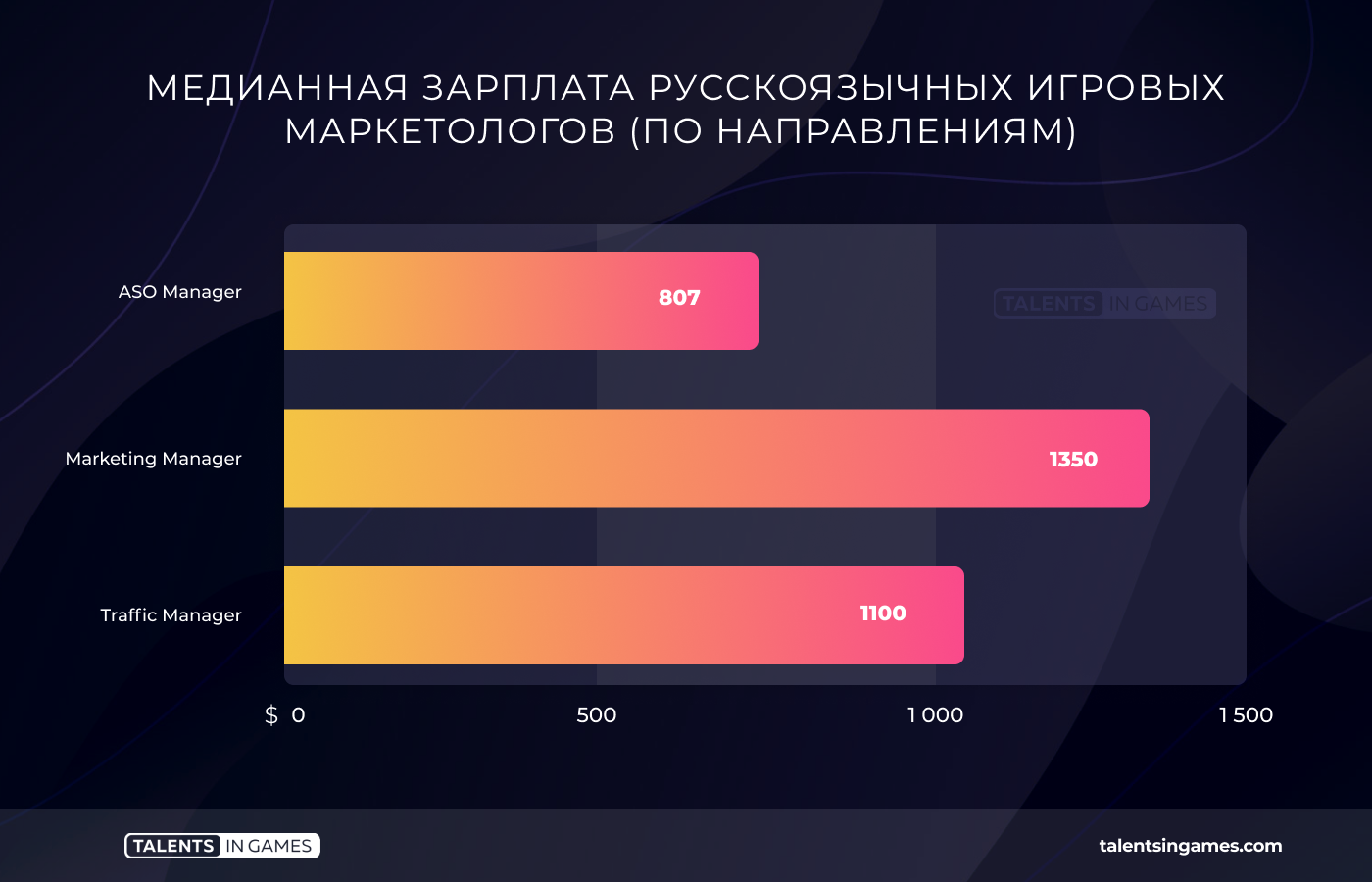
Marketers (88 questionnaires)
The median salary of marketers in the Russian-speaking segment is lower than that of game designers. It is $1,420. At the same time, quite often specialists in this niche receive even less than a thousand dollars.
It turned out to be an interesting and unusual situation with marketers. Most of the responses were received from Moscow (40%). From the rest of the regions, a dozen and a half. Most likely, this suggests that the majority of publishers engaged in marketing are concentrated in the Mother See.
As for the unusual skew in wages (for example, in Moscow there is less than in St. Petersburg and the regions), this is a direct consequence of the mentioned fact. Large companies can afford to train marketers, allow them to “spend” such amounts that small regional teams cannot afford, but at the same time they pay little at the start.
And regions, as a rule, already either hire experienced ones, or try to keep them by all means, including by setting a high salary relative to the location.
According to the data obtained, a marketer is one of those professions whose salary is strongly influenced by experience. The difference in median values between a novice specialist and a leading one is about three thousand dollars.
As for the salaries of marketers by specialization, there is a situation where a universal specialist in terms of median values is paid more generously than narrowly targeted personnel.
Note also:
- almost a third of marketing specialists are women (36.8%);
- there is a very high percentage of people with higher education among marketers (86.2%);
- 20% of leads have fluent English (C1 and higher levels).
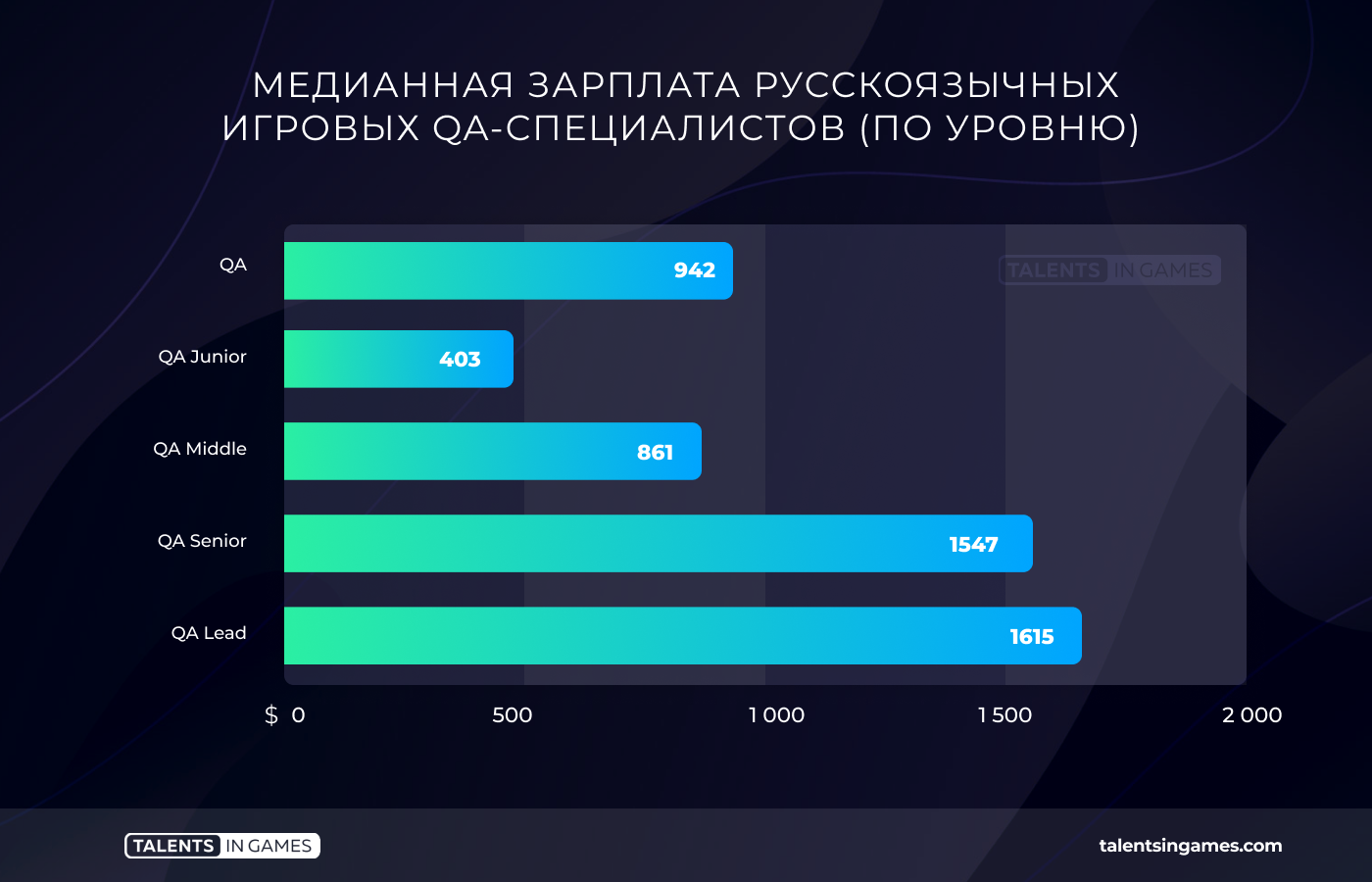
Testers (48 questionnaires)
The median rate for quality control and testing specialists in Russia, Belarus and Ukraine is $942. Here the situation differs little depending on the region. Experience is much more important.
Junos in the QA field have one of the lowest median rates in the industry. It is $403. At the same time, QA-leads can get a lot in the CIS: the highest rate among all respondents was around a little more than $ 3000.
Important: 75% of the QA specialists surveyed are engaged in manual testing. Only 6.3% of the personnel specialize in automatic. The rest resort to both models.
Note also:
- QA is one of the game dev groups that knows English the worst (48.9% have an initial level of English – A1 and A2);
- 70.2% of QA-sphere specialists have completed higher education;
- 61.7% of the cadres are men.
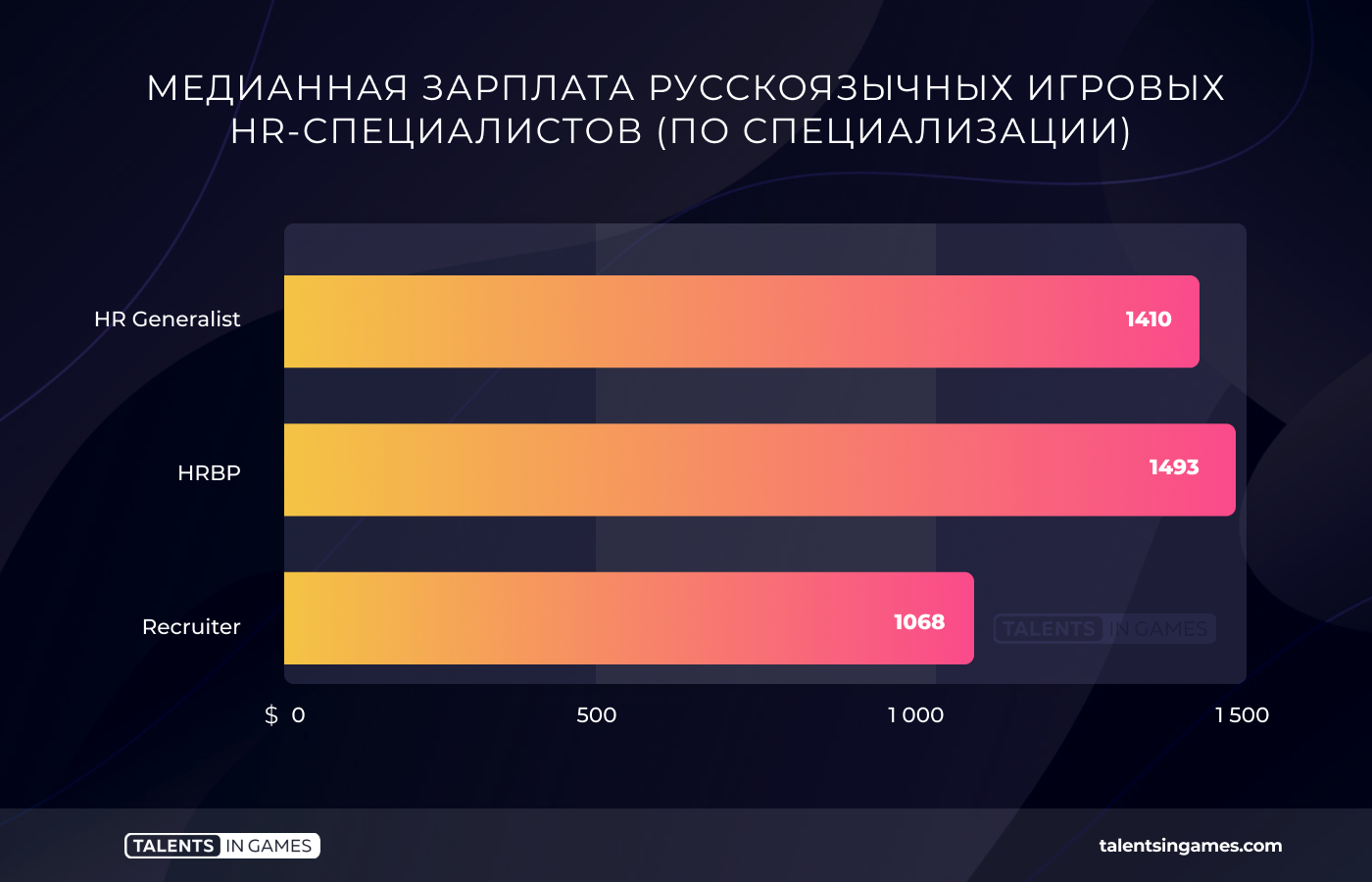
HR specialists (64-questionnaires)
The median salary of professionals responsible for gaming personnel in the Russian-speaking segment of the industry is $1,310. But there is a fundamental nuance here. HR is one of those professions where the salary level strongly depends on the country. In Belarus and Ukraine, the median salary is significantly higher than in Russia, even if compared exclusively with Moscow.
Also of note. The growth rate of HR specialists increases significantly only when moving from the Junior level to the Middle level. Then she goes out onto the plateau. In other words, the labor market does not seem to see much difference between “middle” and “senior”. The rate rises strongly only when a specialist begins to take on a wider range of responsibilities in this area.
There are a lot of specializations within HR now. But most of our respondents were either HR Generalists or recruiters. Also, about a dozen respondents called themselves HR Business Partner (or HRBP, they are responsible for building all HR processes in the company, including analytics).
Also note:
- the opportunity to interview foreign personnel significantly affects the salary, for specialists with a high level of English (from C1 and above), the median rate is $1,759 ($400 more than the base for the entire segment);
- among HR-s, the proportion of specialists who have received a full higher education is very high (90.5%);
- the group is dominated by women, followed by men less than 5%.
Support specialists and community managers (30 questionnaires)
In an ideal world, support specialists and community specialists should be separated. However, in reality, too often there are situations when the job responsibilities of both directions are combined. At the same time, if we do not take into account universal specialists, then the support staff is very different from the community staff in terms of background and salary. But we’ll stop there a little later.
The median salary in the whole segment is $1,000. In Russia, a little less — $ 942. The lower salary that we fixed is $215, the highest is $2,600.
The median salary of personnel who are engaged only in community development is twice as high as the median salary of support staff. Those who are engaged in both receive less personnel than specialists who are “sharpened” only for working with the community.
The difference may well be explained by the fact that a different level of competence is required for the development of the Western community. In particular, more fluent English. We were prompted to this version by the fact that the English level of support does not exceed B1, and 50% of the surveyed community managers have it higher than C1. Simply put, one of the important factors affecting the salary in this niche is the knowledge of English.
Also note:
- among the support specialists, the smallest number of people with a completed education is 62.1% (the average level of the “clean” community is higher – 70%, and the “clean” support is lower);
- 65.5% of specialists are men;
- the main age is from 25 to 34 years (79.3% have it, but there are relatively few young professionals, only 10.3% are under 24 years old).
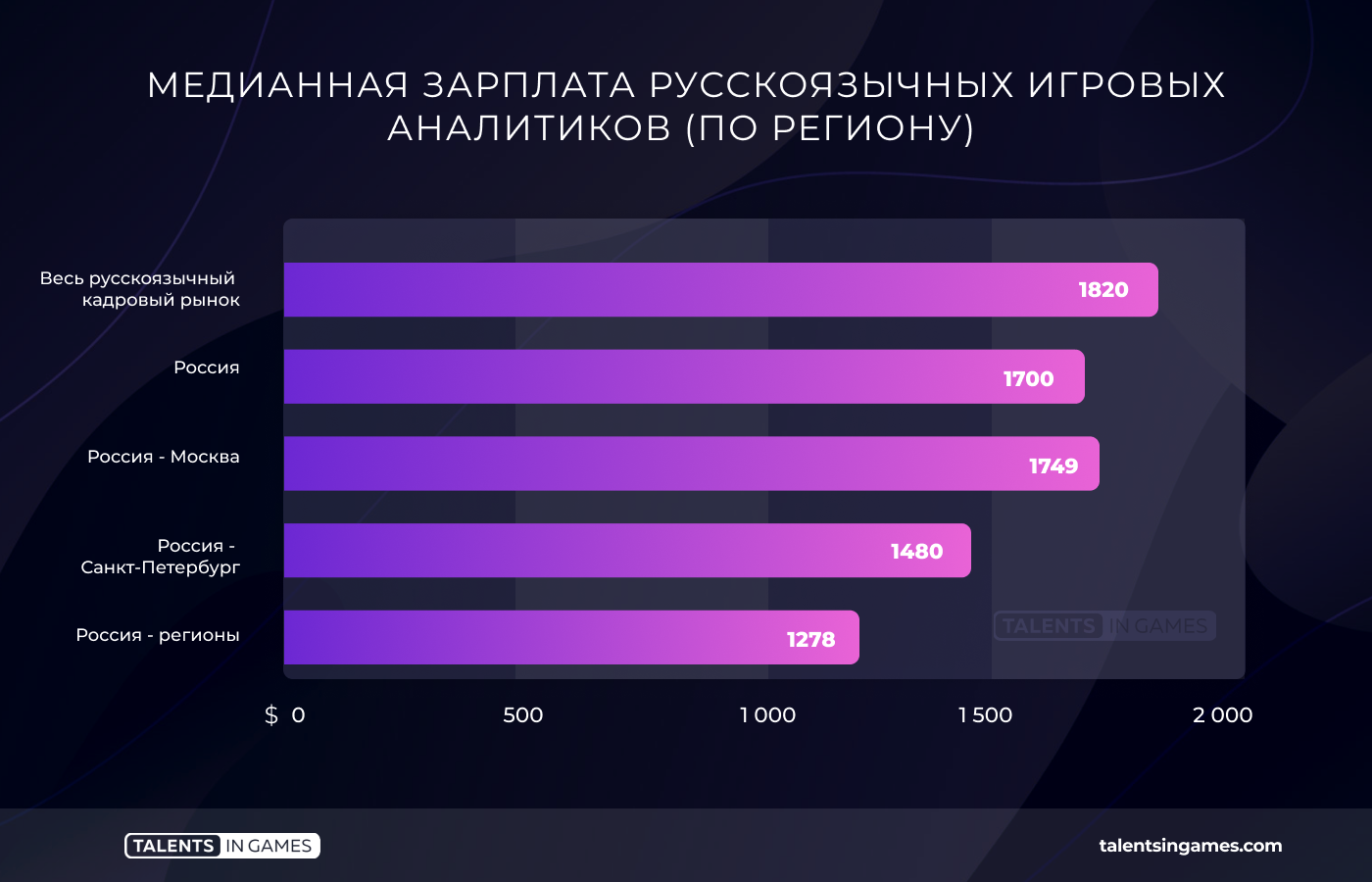
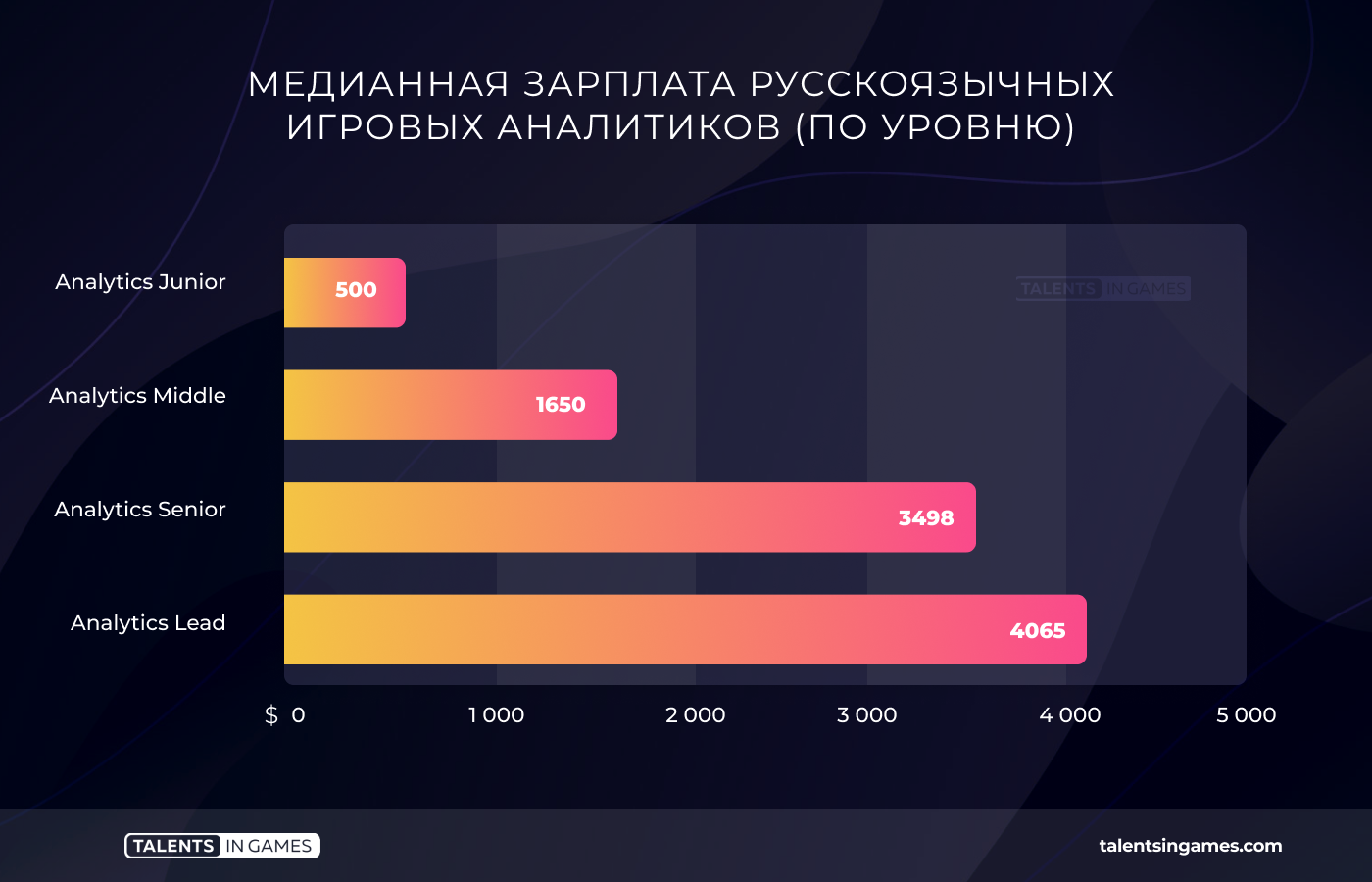
Analysts (41 questionnaires)
Here we are faced with an exceptional situation when more applications for the specialty came from Cyprus than from Ukraine or Belarus (of which there were very few, at the level of two or three from each region, so we are not considering them this time).
Now to the numbers.
The median salary of an analyst in the Russian-speaking segment of the gaming industry is $1820. In Russia, this value is less — about $ 1,700.
The salary of an analyst primarily depends on his level. For example, leads located in Cyprus may well count on $4,000 per month. At the same time, seniors in Russia also in some cases have a rate that reaches this level, although the median value is lower.
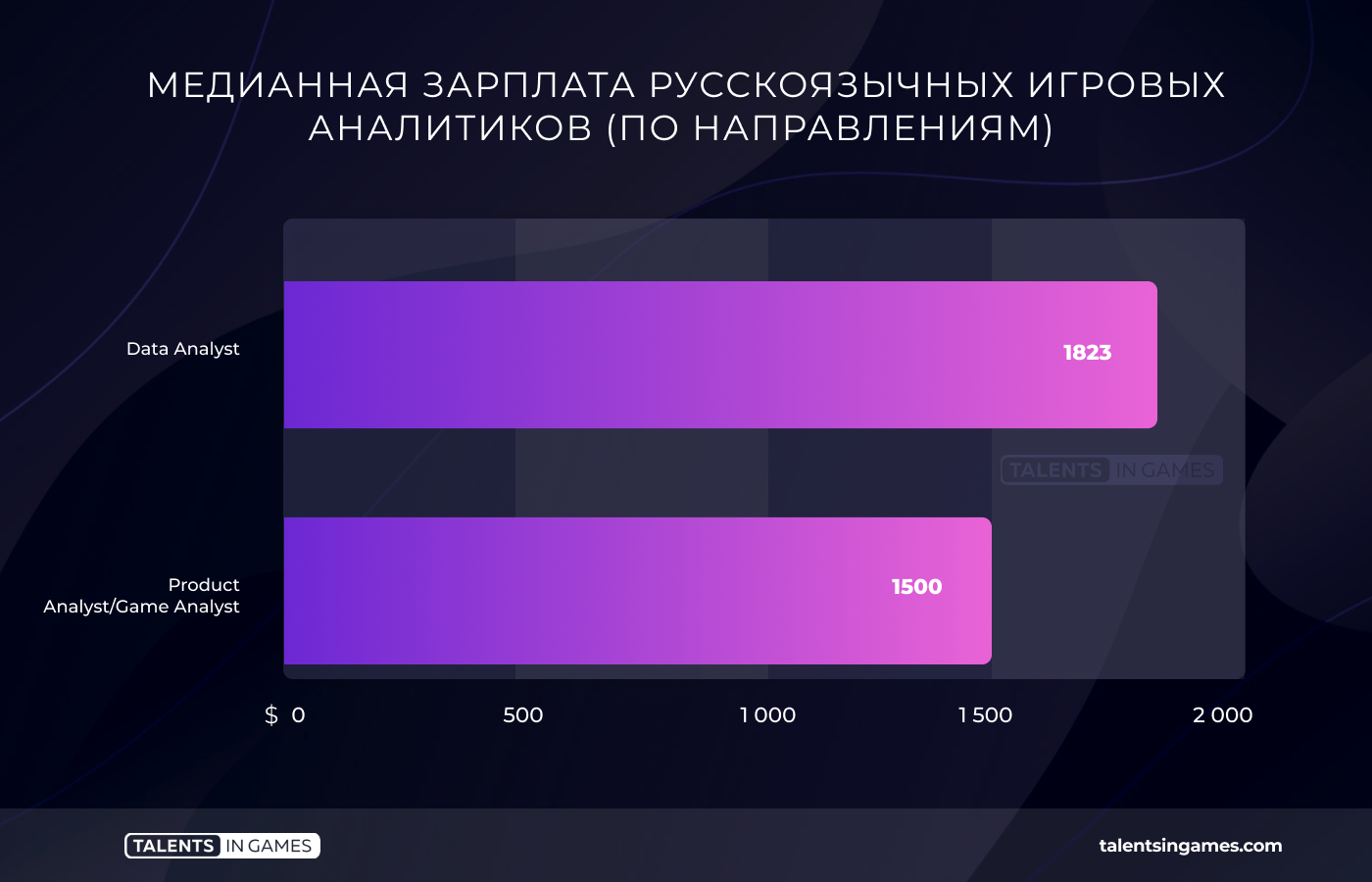
If we talk about the difference in salary between specializations, then there is one. Product analysts usually receive less than those who work with data analysis. The median bid of the latter is higher by $300.
Also note:
- there are quite a lot of young analysts (in 22.5% of cases, niche specialists are less than 25 years old);
- 7.5% of analysts have an academic degree (this is the highest value in the industry);
- 70% of game analysts are men.
Business Development Specialists (19 questionnaires)
The median salary of business owners (this also includes pure sales) in the Russian-speaking segment of the gaming industry is one of the highest in the market. It is $2,730 (including, if separately counted in Russia). Moreover, already at the Middle level there are rates of $ 2000 per month.
Among the important we note:
- 45.4% of business development specialists are women;
- 94.4% of specialists have completed higher education;
- 77.6% of business owners have an English level of C1 or higher (fluency).
Sound specialists (19 questionnaires)
The median salary for sound specialists is $1,160 ($100 less in Russia). There are very few high rates (around $2000).
The most common “sound” profession in our industry, judging by the answers, is a sound designer. 66.7% of respondents identified themselves as such. Their median bid is $817.
Also note:
- the age of the majority (72.2%) is from 25 to 34 years;
- 94% are men;
- 72.2% have a higher education.
Other professions
A number of other areas received fewer questionnaires for a full-fledged analysis (about a dozen per segment). Therefore, in the table below, we will give only median values for them.
Regarding this table, we note the following:
- the low salary level of admins explains the sample, where there were many entry-level specialists;
- localizers, on the contrary, turned out to be one of the most “age” groups, a quarter of respondents are over 45 years old;
- women prevail among office managers and PR specialists.
Conclusions
1.
In general, salaries in the gaming industry in Belarus and Ukraine are higher than in Russia. Sometimes much higher. We tend to explain this as follows:
- both in Belarus and in Ukraine, the salary in gaming IT is pegged to the dollar, so it does not suffer from inflation (in Russia, such a peg is not common, people receive money in rubles and agree on a salary in rubles, too, without converting everything into foreign currency);
- In Belarus, the personnel market is much smaller than in Russia, which means that there is higher competition for them. This leads to a salary race, which is aimed at both retaining staff and attracting the missing ones from competitors.
- In Ukraine, the bulk of the gaming IT sector works either outsourced or in local offices/representative offices of Western companies that can afford to pay salaries higher than in the whole region.
2.
If we talk specifically about specialists and do not raise the topic of management, then the most highly paid areas in the gaming industry today are analytics and business development.
The least paid specialists directly involved in the creation of game content are artists. Their median salary in the market is at the level of testers.
P.S.
In the survey, we also asked respondents which company they would like to work for. The top five most desirable companies, along with Activision Blizzard and Ubisoft, included Playrix, which is the most commercially successful gaming company based on the territory of the former USSR.